Podman Desktop AI Lab - 40 minutes
1. Goals of this lab
Your first step is to start learning and experimenting with AI for enterprise applications. In this section, you’ll understand how you can work with the Podman AI Lab for building AI-enabled applications. You will accomplish this with the following steps:
-
Learn about Podman AI Lab and how it can accelerate developer productivity for building applications using Generative AI.
-
Test out the different features of the AI Lab, including the model catalog, playground environments, and more.
-
Deploy a basic summarization application, upload a claim, and view summarization to quickly understand how AI can assist with insurance claims.
-
Change the prompt, restart, and observe changes.
2. The AI Journey for an Application Developer
More Than 80% of Enterprises Will Have Used Generative AI APIs or Deployed Generative AI-Enabled Applications by 2026
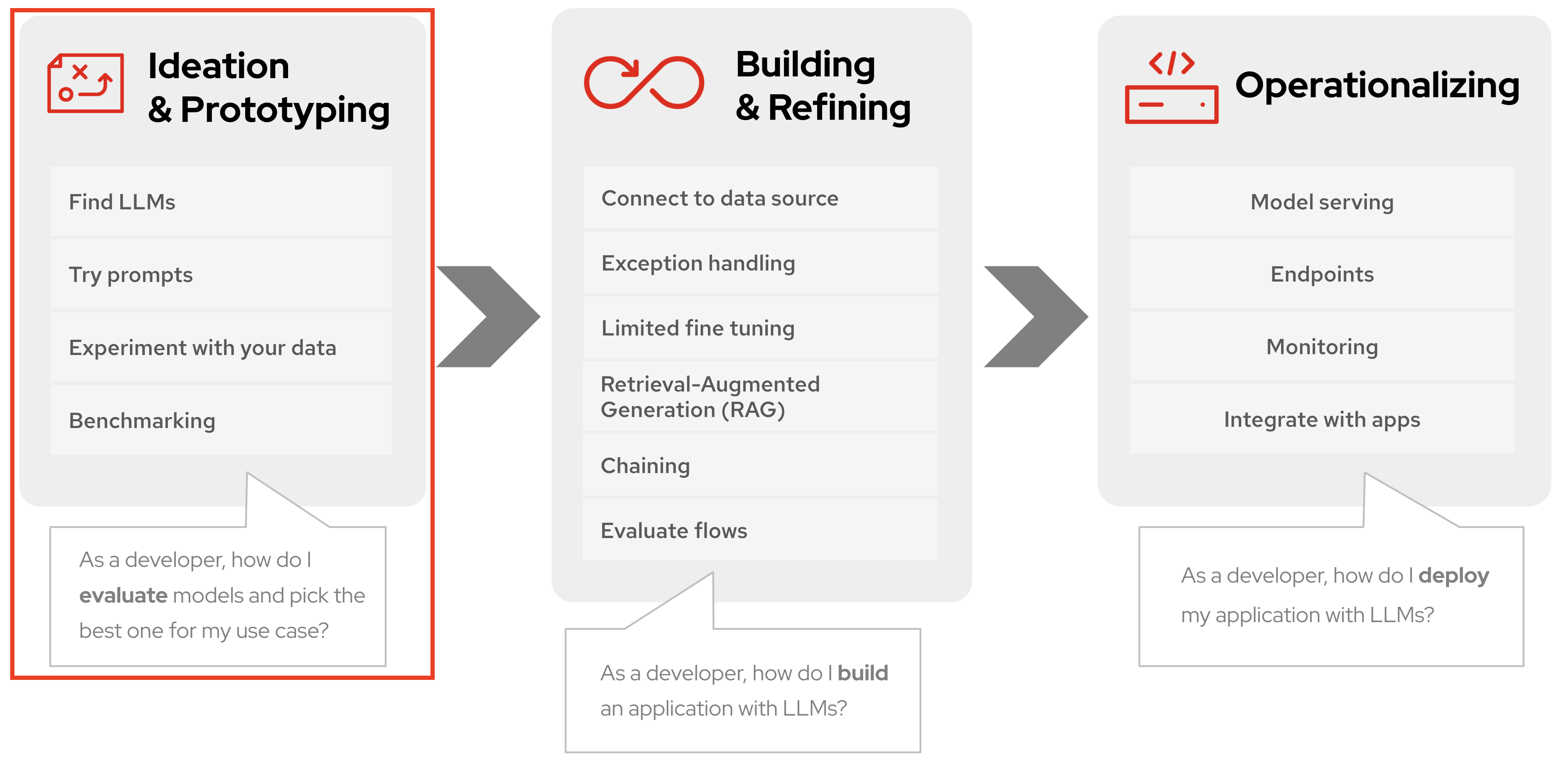
This is why, as a developer at Parasol Insurance, it’s important to understand the different steps of the journey to learning, understanding, and working with AI:
-
Ideation & Prototyping - How do I evaluate models and pick the best one for my use case?
-
Building & Refining - How do I build an application with LLMs?
-
Operationalizing - How do I deploy my application with LLMs?
This module will focus on Ideation and Prototyping.
3. Getting Started with Your Developer Environment for Generative AI
3.1. Understanding Podman Desktop and AI Lab
We’ll be using Podman Desktop, an open-source graphical interface for managing images, containers, and pods on a local system. It provides a user-friendly way for developers in our organization to work with containerized applications and services. The AI Lab extension for Podman Desktop is a powerful tool that allows developers to explore and experiment with various AI models and applications locally. We’ll learn how to use it to kick-start our discovery and usage of generative AI.
3.2. Key Components of Podman AI Lab
With Podman AI Lab, we’re provided a curated catalog of open-source recipes, ready-to-use models, and playgrounds for common generative AI use cases. The main components include:
-
Recipes Catalog: A collection of pre-built AI applications and use cases that demonstrate real-world implementations of AI models.
-
Open Source Models: A curated list of AI models that can be easily downloaded and used, with information on their licenses and capabilities.
-
Playground Environments: Interactive spaces to test and experiment with different models, allowing developers to specify model parameters and observe results.
-
Model Serving: Capability to run local inference servers for AI models, providing an OpenAI-compatible endpoint for application integration.
4. Exploring the Podman AI Lab Interface
Your developer environment includes Podman Desktop with an AI Lab extension that you will install, allowing you to instantly get started exploring and working with Generative AI in your application development workflow.
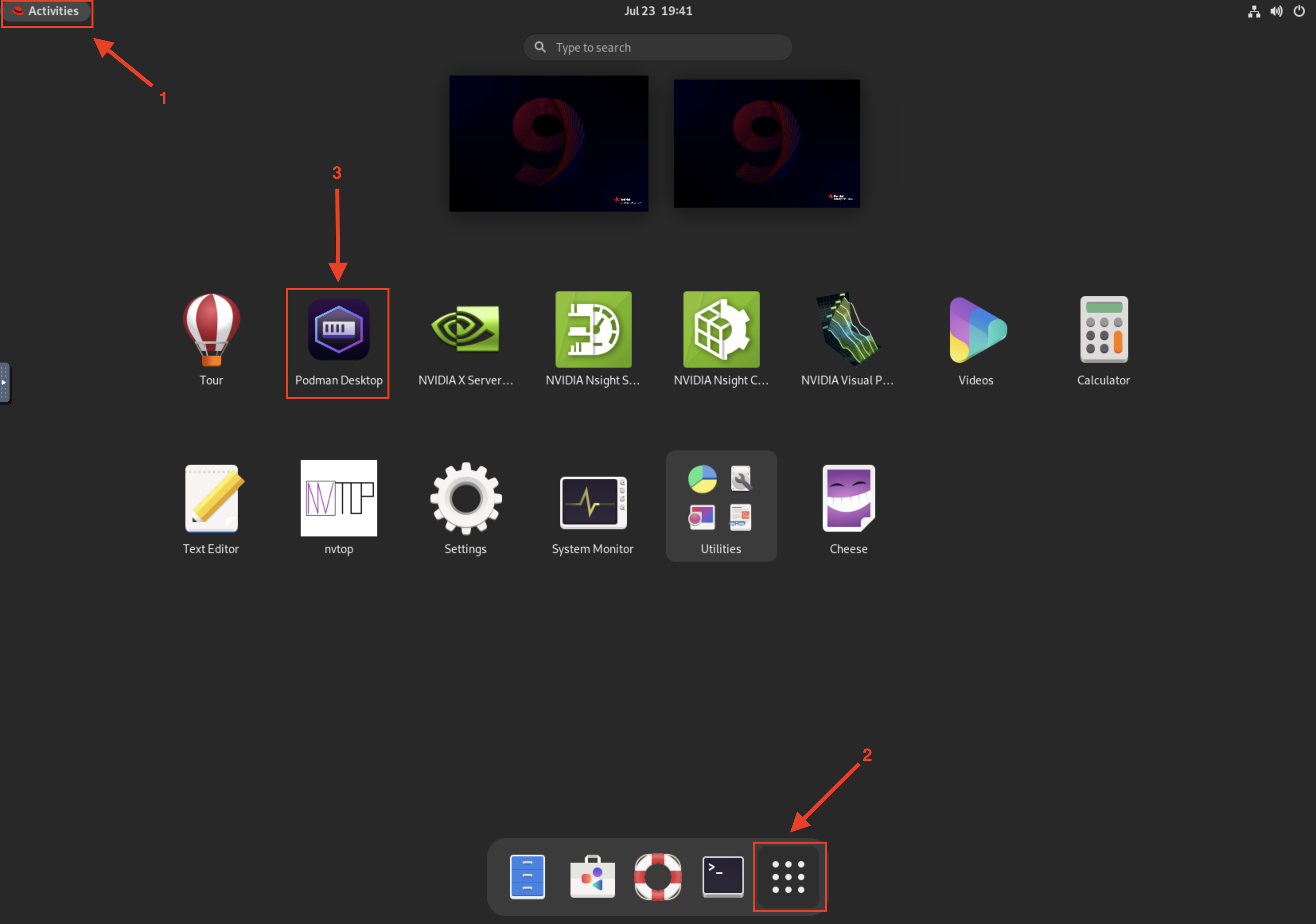
4.2. Install Podman AI Lab
At the initial screen, click Go to Podman Desktop:
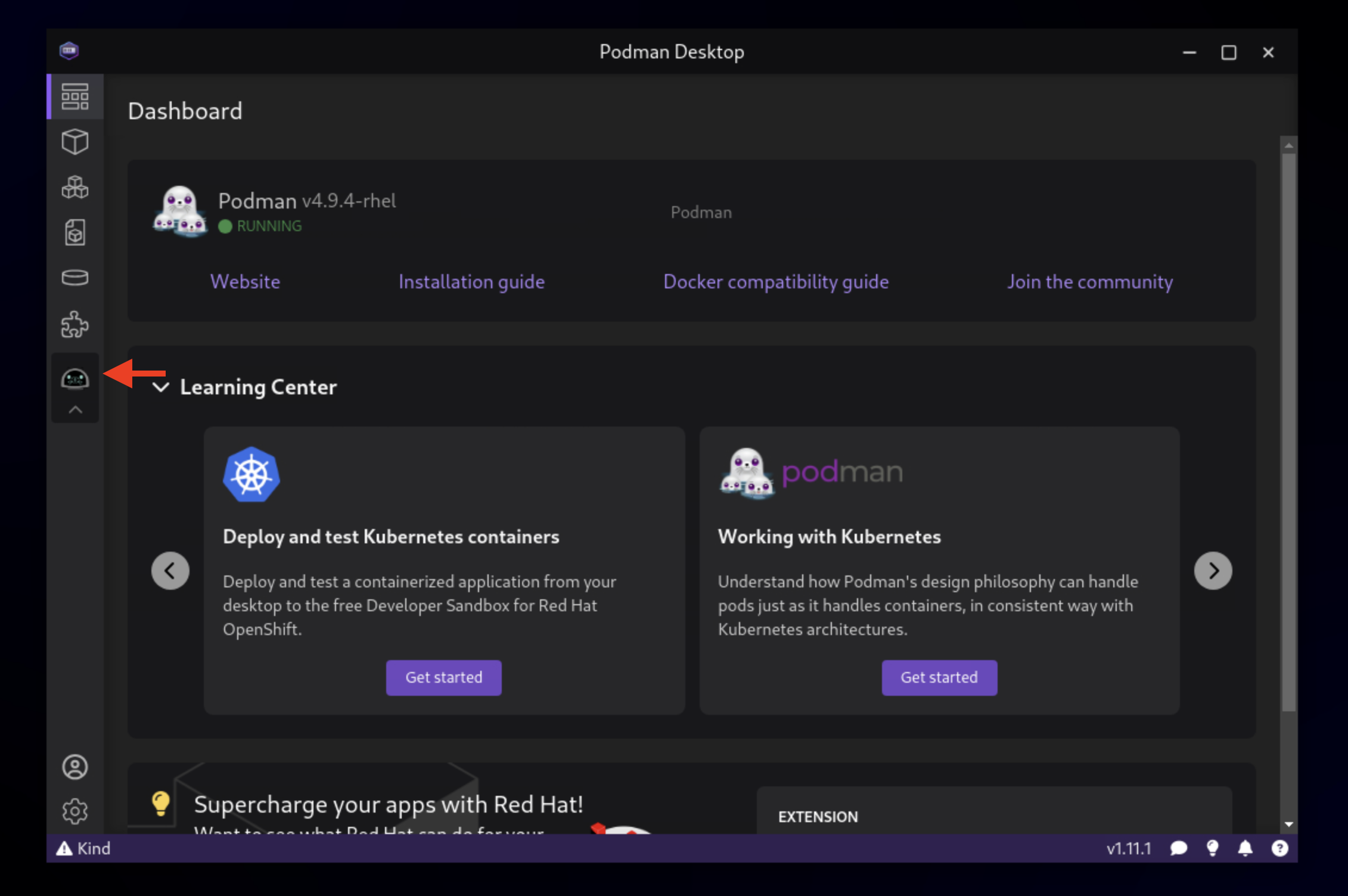
You should land on the Dashboard as shown.
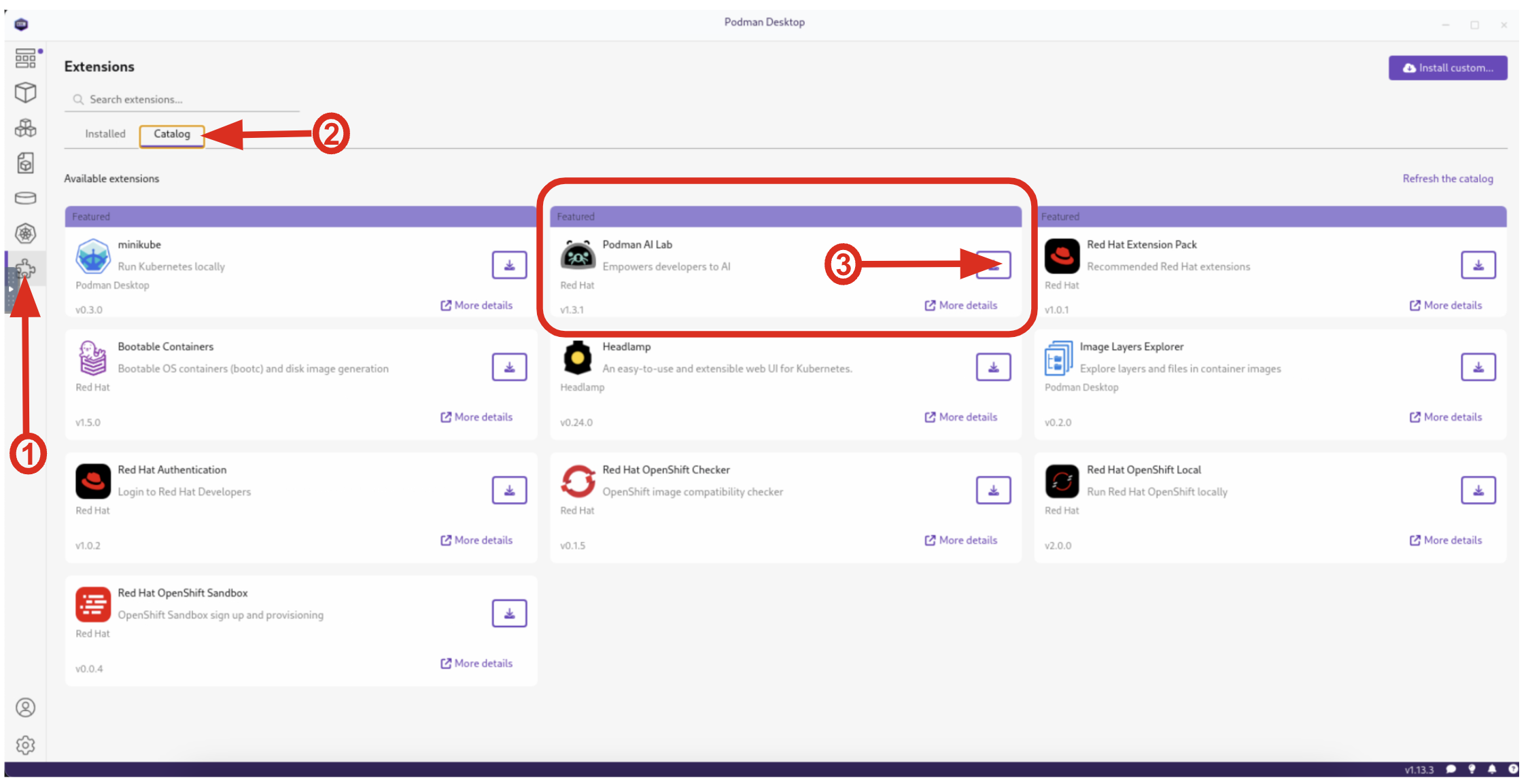
Click the Extensions puzzle piece icon on the left, and navigate to the Catalog tab. You should see the Podman AI Lab Extension in the Featured section. Click the Download button to install it. Once installed, you should see the new icon on the left for AI Lab.
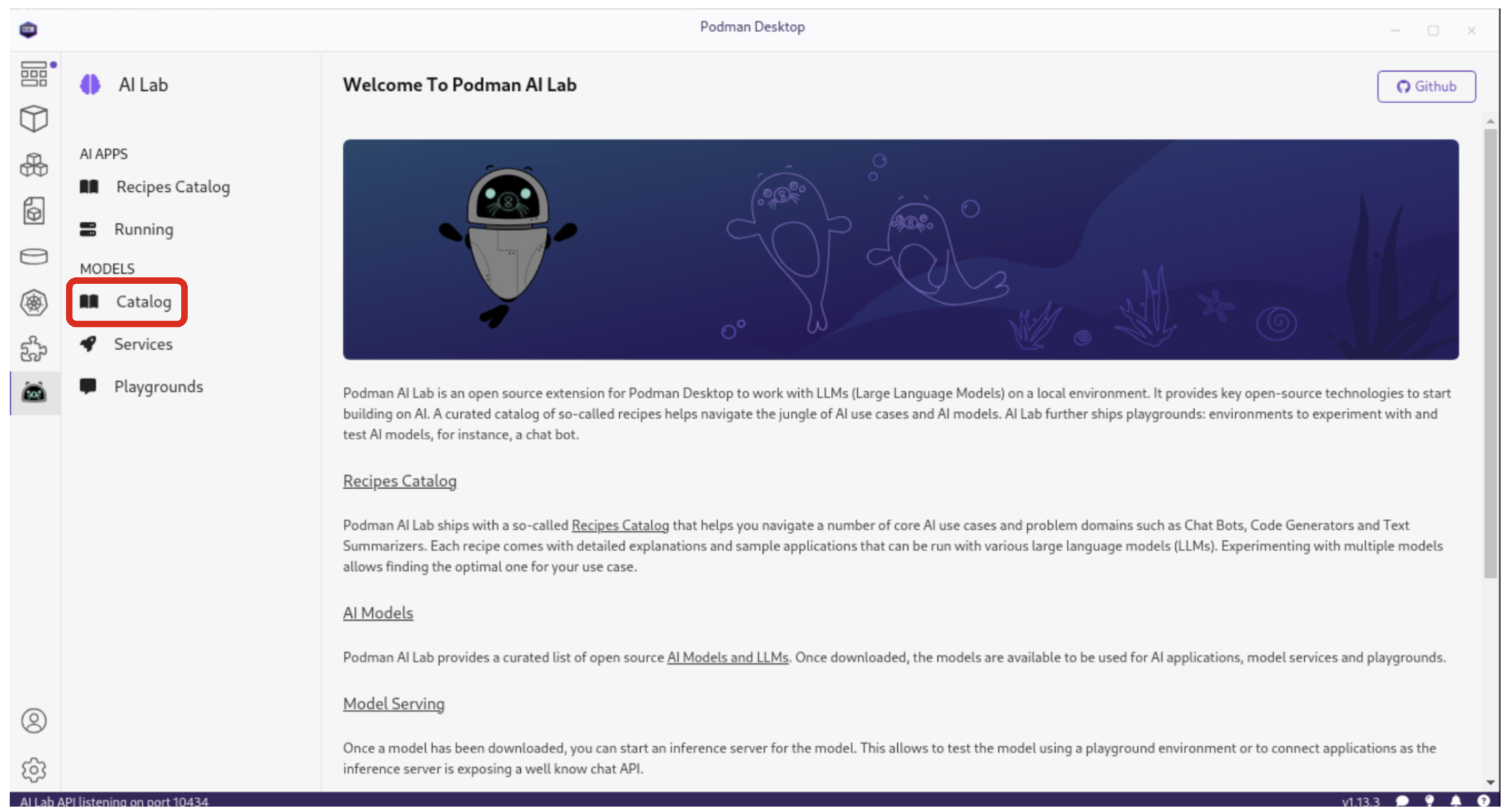
4.3. Viewing the Model Catalog
The Model Catalog is a key component of Podman AI Lab, providing developers with a curated list of open-source AI models and Large Language Models (LLMs). Select the Models / Catalog from the menu.
The Model Catalog interface is organized into four distinct tabs, each serving a specific purpose:
-
All: Displays the complete list of catalog models. Models that have been downloaded are easily identifiable by their solid icon.
-
Downloaded: Shows only the models that have been stored locally on your machine, ready for offline use.
-
Imported: Lists any custom models you’ve imported that weren’t originally part of the catalog. These could be models you’ve trained yourself or obtained from other sources, via
.ggufformat. -
Available: Presents all catalog models that are yet to be downloaded.
|
All models in the Podman AI Lab catalog are licensed under Apache 2.0. This permissive open-source license grants users the freedom to use, modify, and distribute the software, while also providing patent rights. |
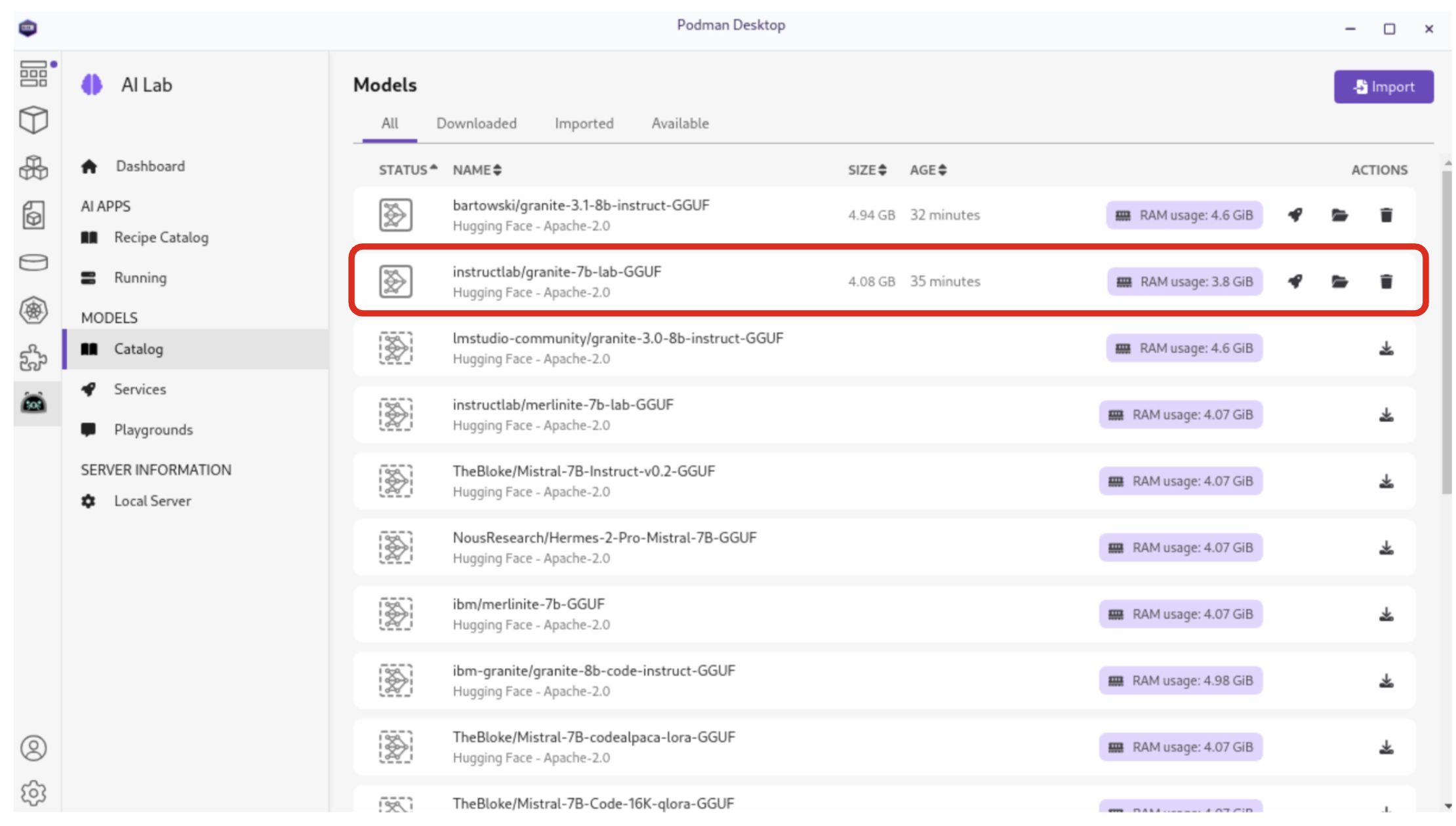
If the icon next to the granite_7b-lab model is a solid box, then the instructlab/granite-7b-lab-GGUF model has been pre-installed for you. if not, click the Download button to download it (this should only take a minute or two):
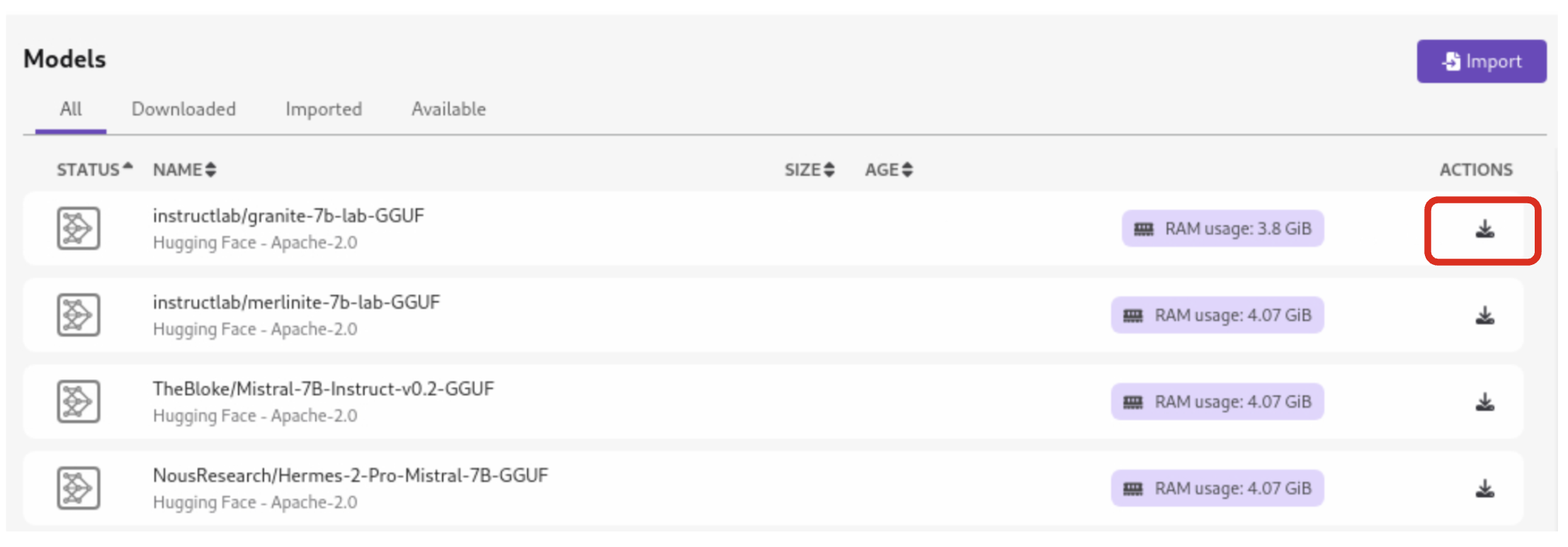
| Before moving on to the next section, ensure that the model has completed downloading, or you may encounter issues when trying to serve it. |
4.4. Model Serving and Integration
Model serving is a crucial step in making AI models accessible for application integration. Podman AI Lab simplifies this process by allowing you to run inference servers for downloaded models, exposing them through OpenAI-compatible API endpoints. From the AI Lab menu, select Models / Services.
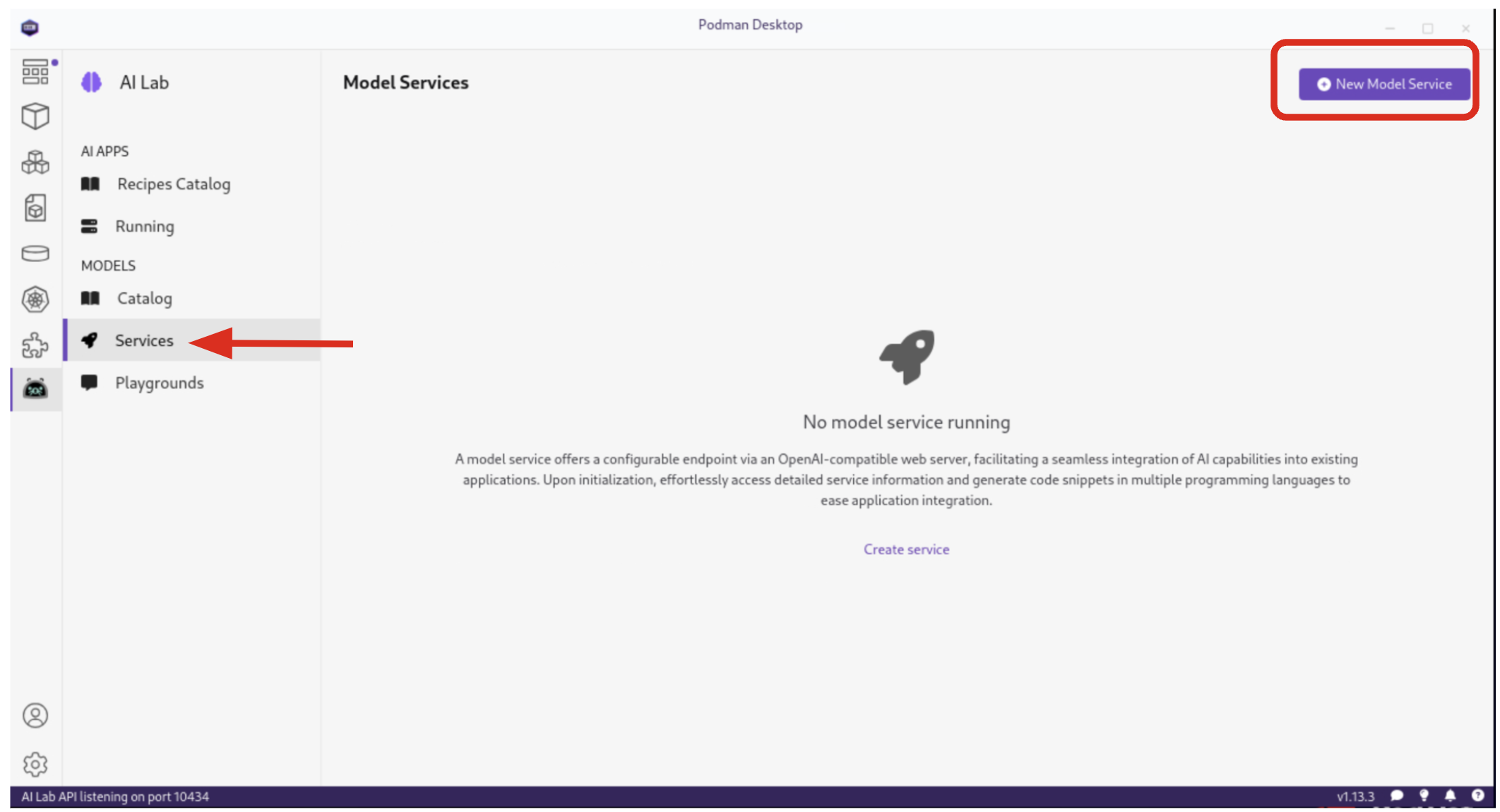
By selecting New Model Service, you can choose a pre-downloaded model from the dropdown menu and start an inference server for it. This action deploys a containerized model service that exposes the AI model via a REST API endpoint on a random port.
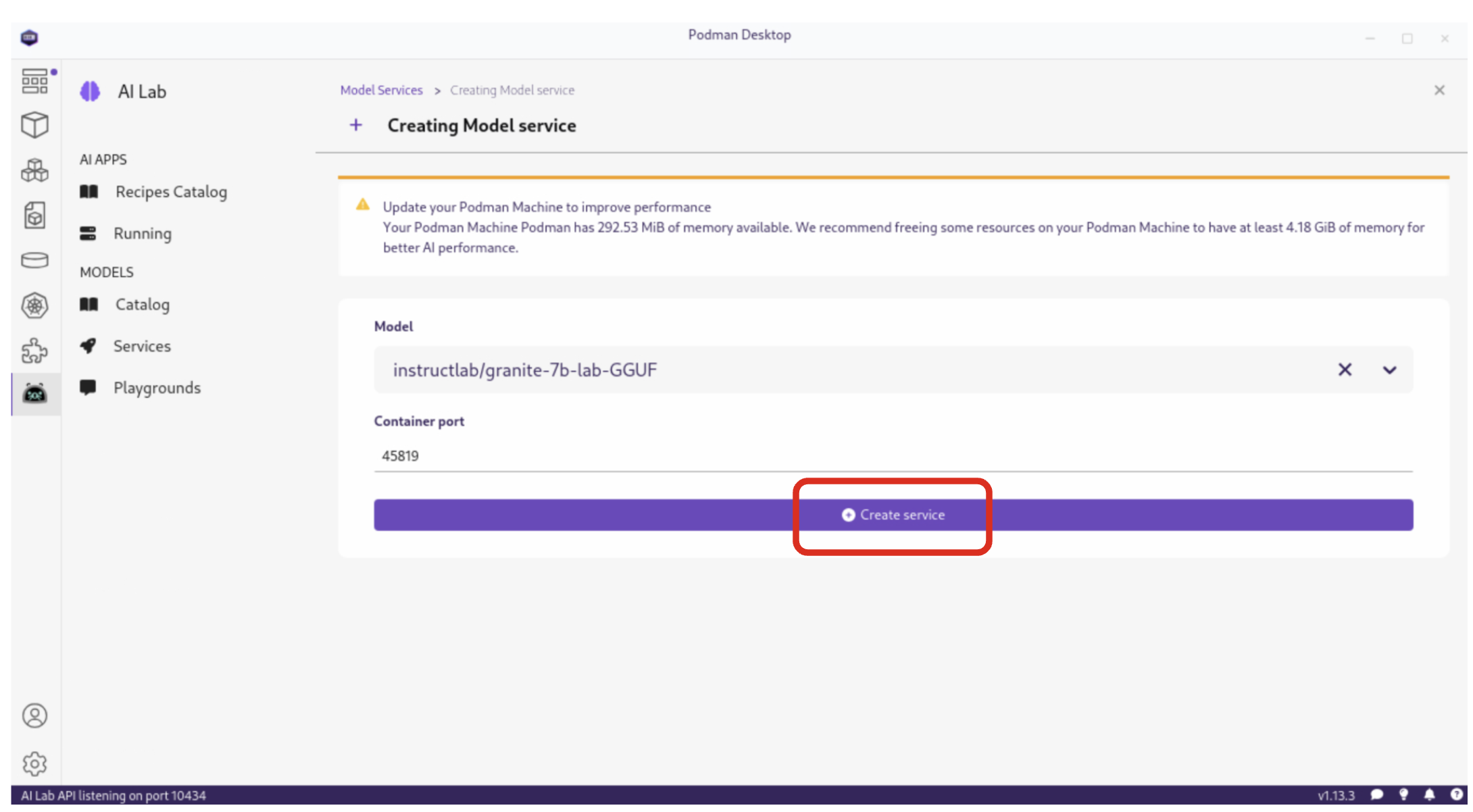
Once completed, click the Open service details to see the model service details dashboard, which provides essential information for integrating the model into your applications:
-
Inference Endpoint URL: Provides the local URL (inference endpoint) for the model.
-
Model: Displays the model name, license, and source repository.
-
Client Code: Offers integration code snippets in various programming languages.
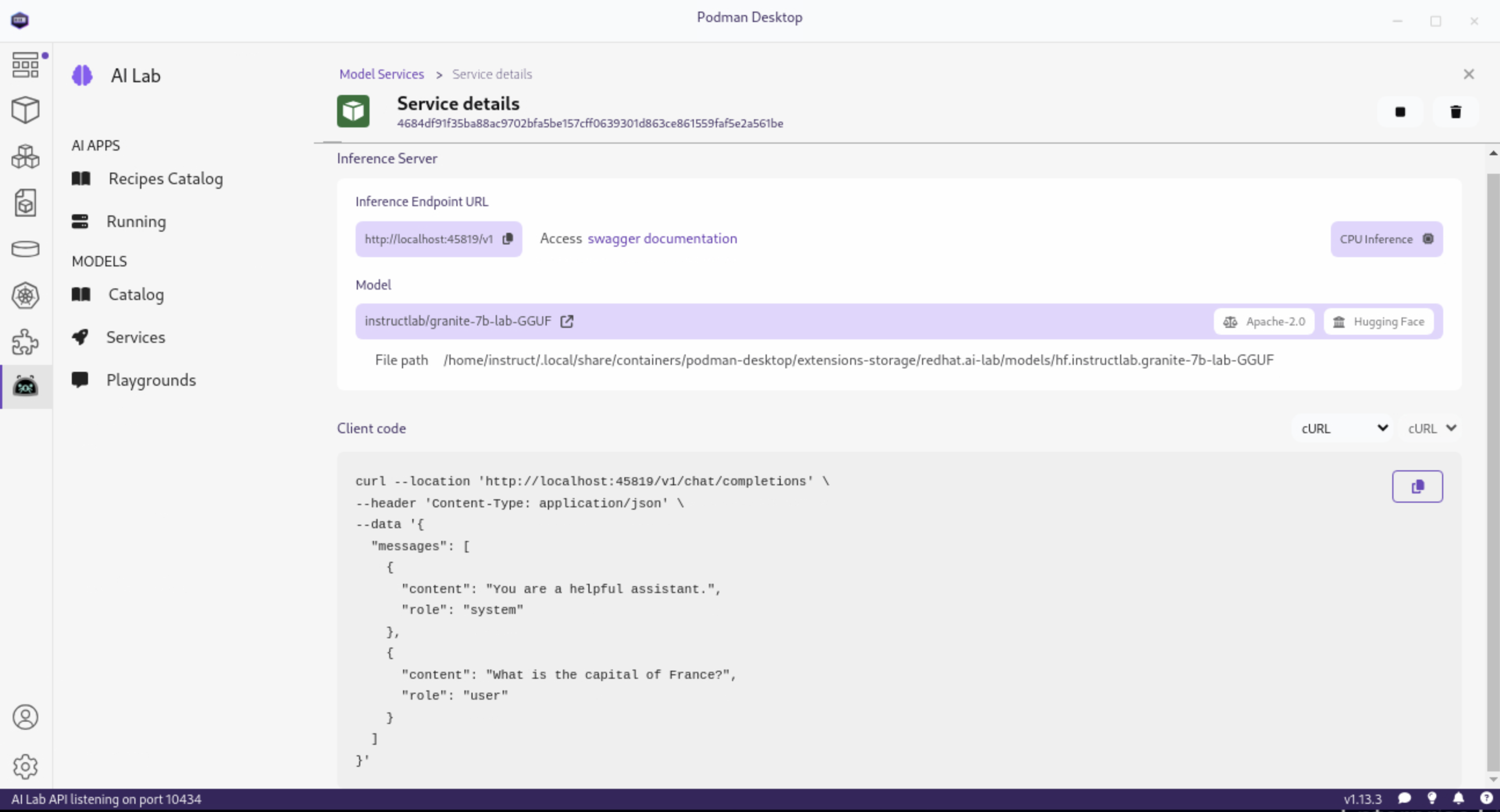
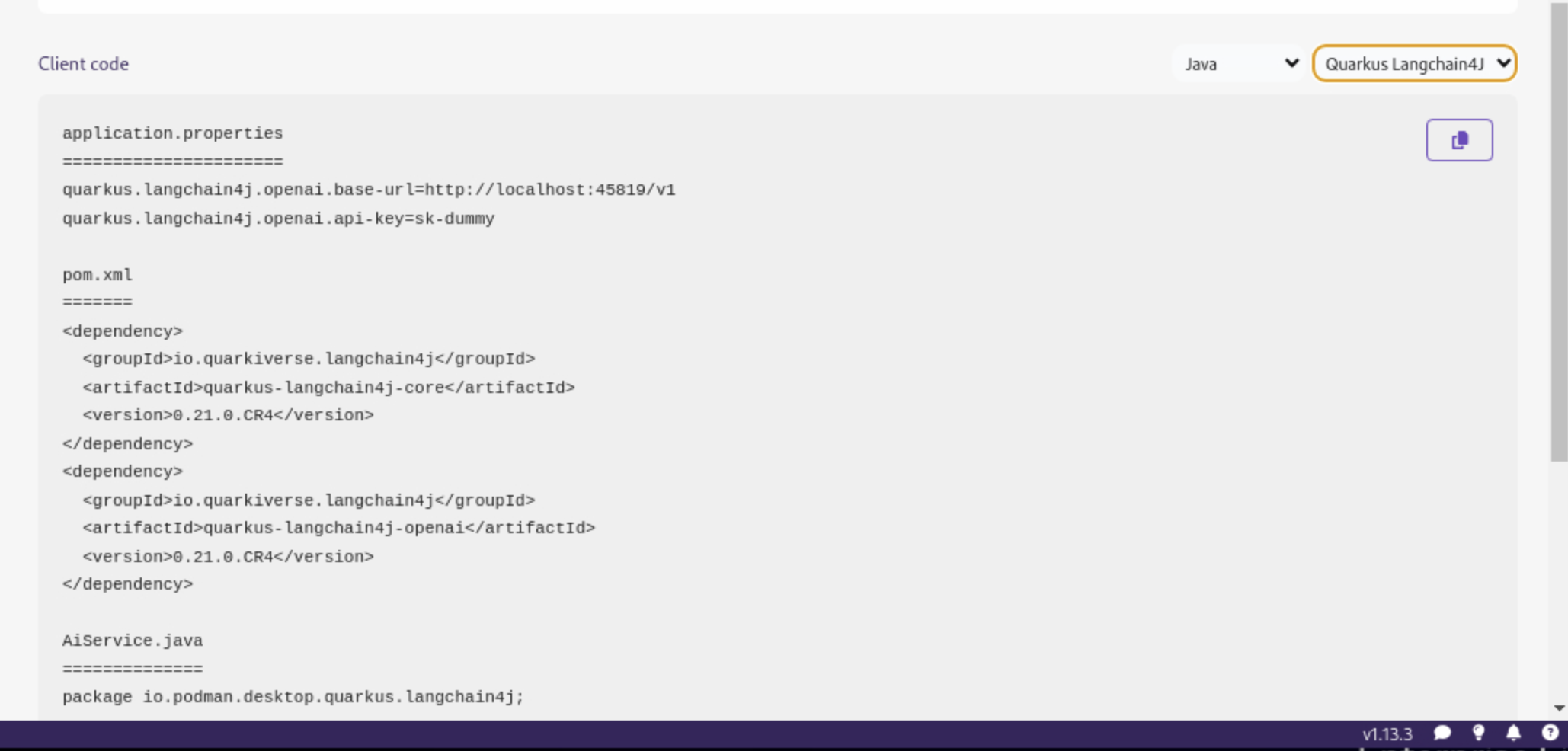
Specifically, the Client Code section provides developers with code snippets in popular programming languages, such as Java, Python, JavaScript, and cURL, among others, to help quickly integrate the model into their applications. Typically, this includes the following information:
-
Endpoint connection details: The URL and necessary headers for connecting to the model service.
-
Sample prompt: A basic example query to test the model’s functionality.
4.5. Testing out Playground Environments
The AI Lab Playground is a powerful feature that allows you to experiment with available models in a local environment. It provides an intuitive user interface for exploring model capabilities, accuracy, and finding the best model for your use case.
From the AI Lab menu, select Models / Playgrounds.
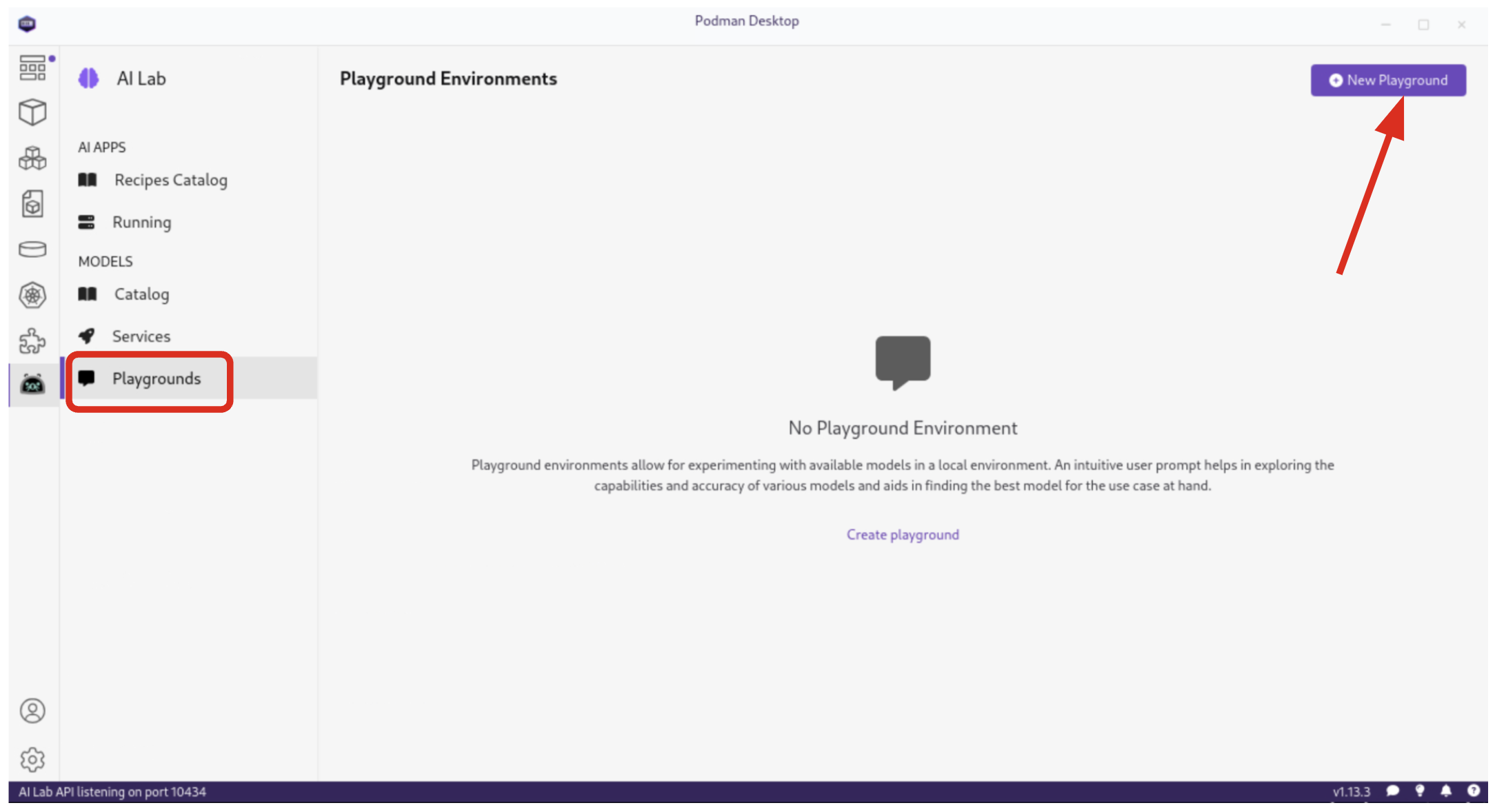
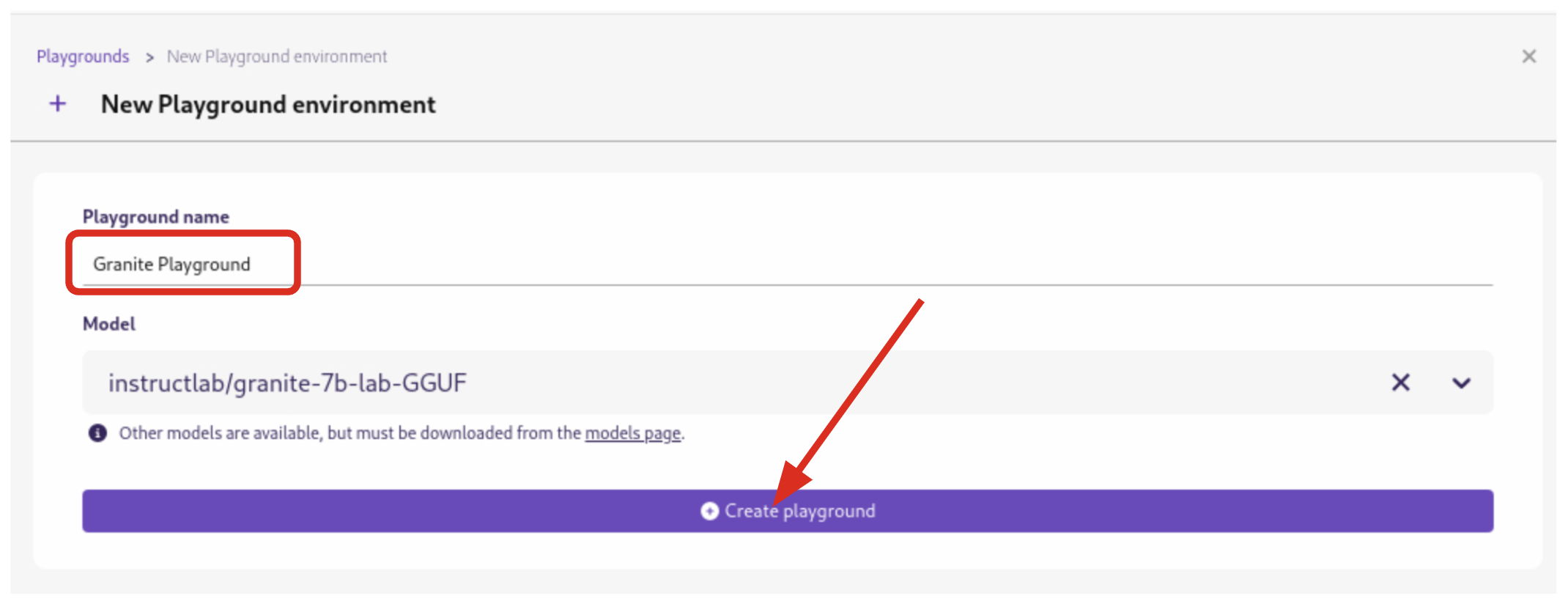
By selecting New Playground, you can select a pre-downloaded model from the dropdown menu and start experimenting with it.
This action deploys two key components:
4.5.2. An ai-lab-playground-chat container that provides the user interface for model interaction
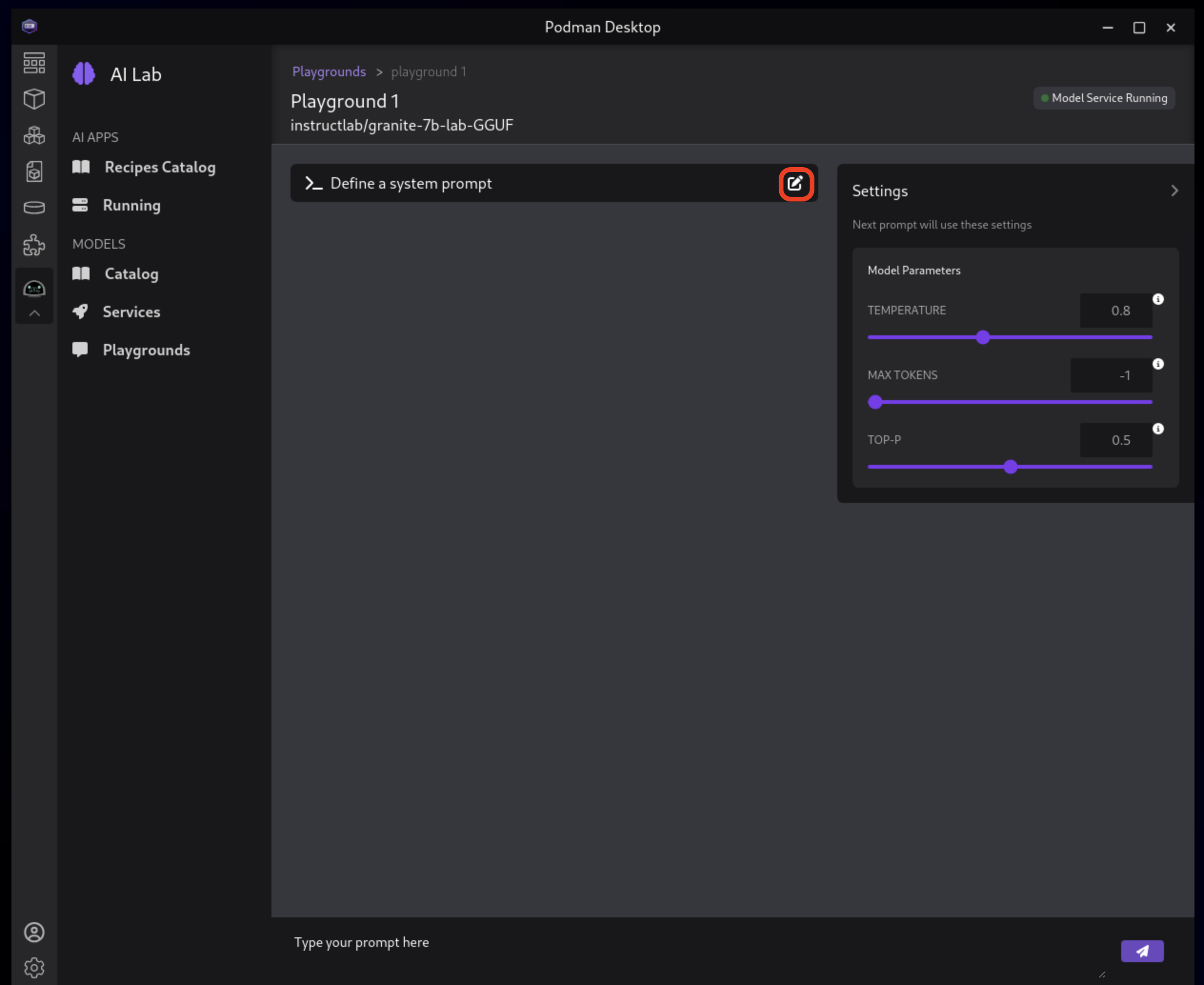
The Playground interface offers several technical features for fine-tuning model behavior:
-
System Prompt:
-
Located at the top of the chat interface, this allows you to set the context and behavior of the AI model.
-
-
Hyperparameter Tuning: The Settings widget on the right side provides access to crucial parameters:
-
Temperature: Controls the randomness of the model’s responses. Lower values produce more deterministic outputs, while higher values introduce more randomness.
-
Max Tokens: Limits the number of tokens generated by the model, which can help prevent overly verbose responses.
-
Top P: Determines the number of tokens to consider for each step of the model’s generation process. Higher values can lead to more diverse responses.
-
By systematically testing various configurations and prompts related to insurance scenarios, developers can gain insights into model performance and identify optimal settings for specific use cases within Parasol Insurance’s applications. This process of experimentation and analysis in the Playground environment is crucial for understanding model capabilities and limitations before integration into production systems.
Now let’s play with it a bit:
4.5.5. Paste in the following text
Click the checkmark to save the system prompt
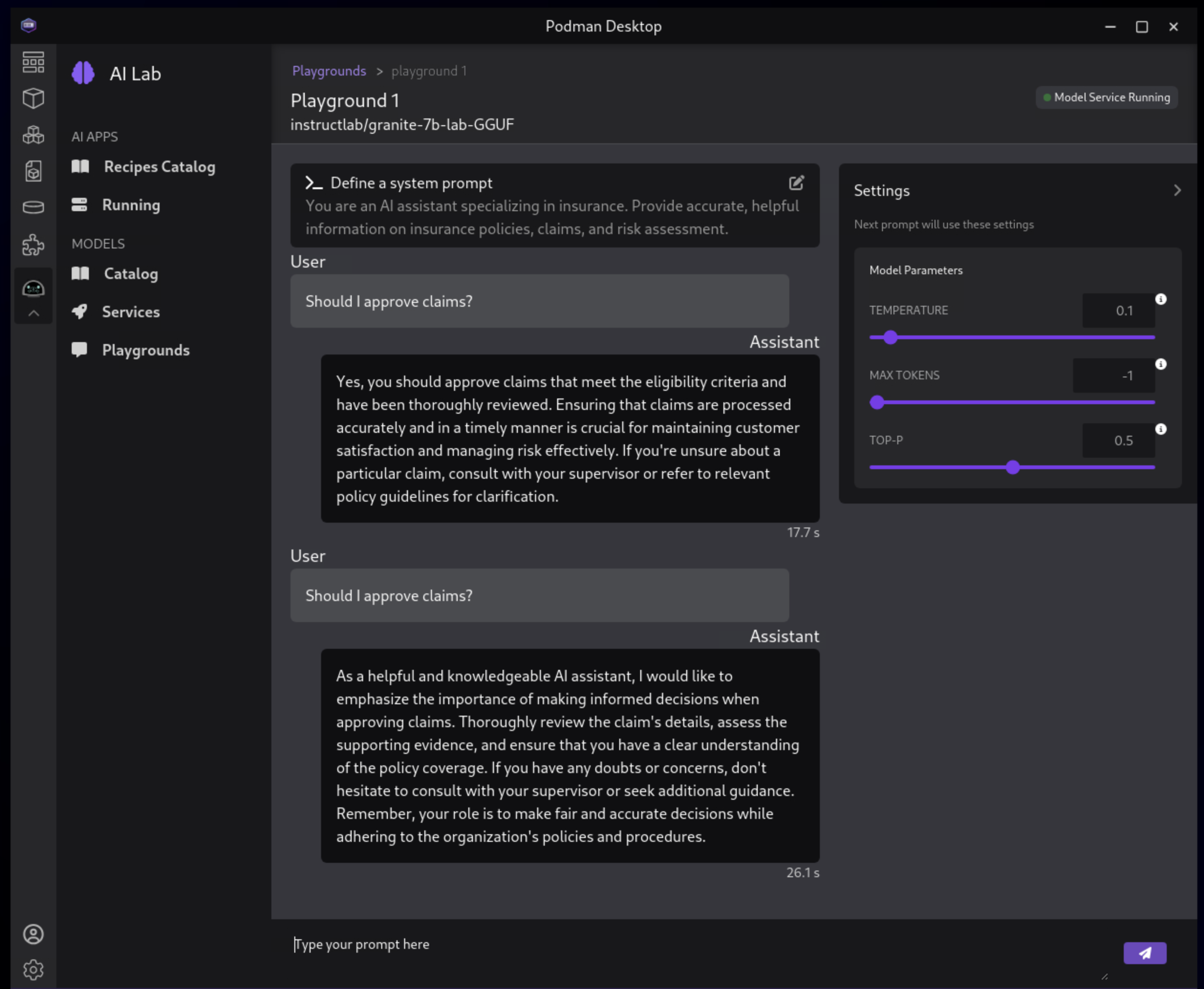
You are an AI assistant specializing in insurance.
Provide accurate, helpful information on insurance policies, claims, and risk assessment.
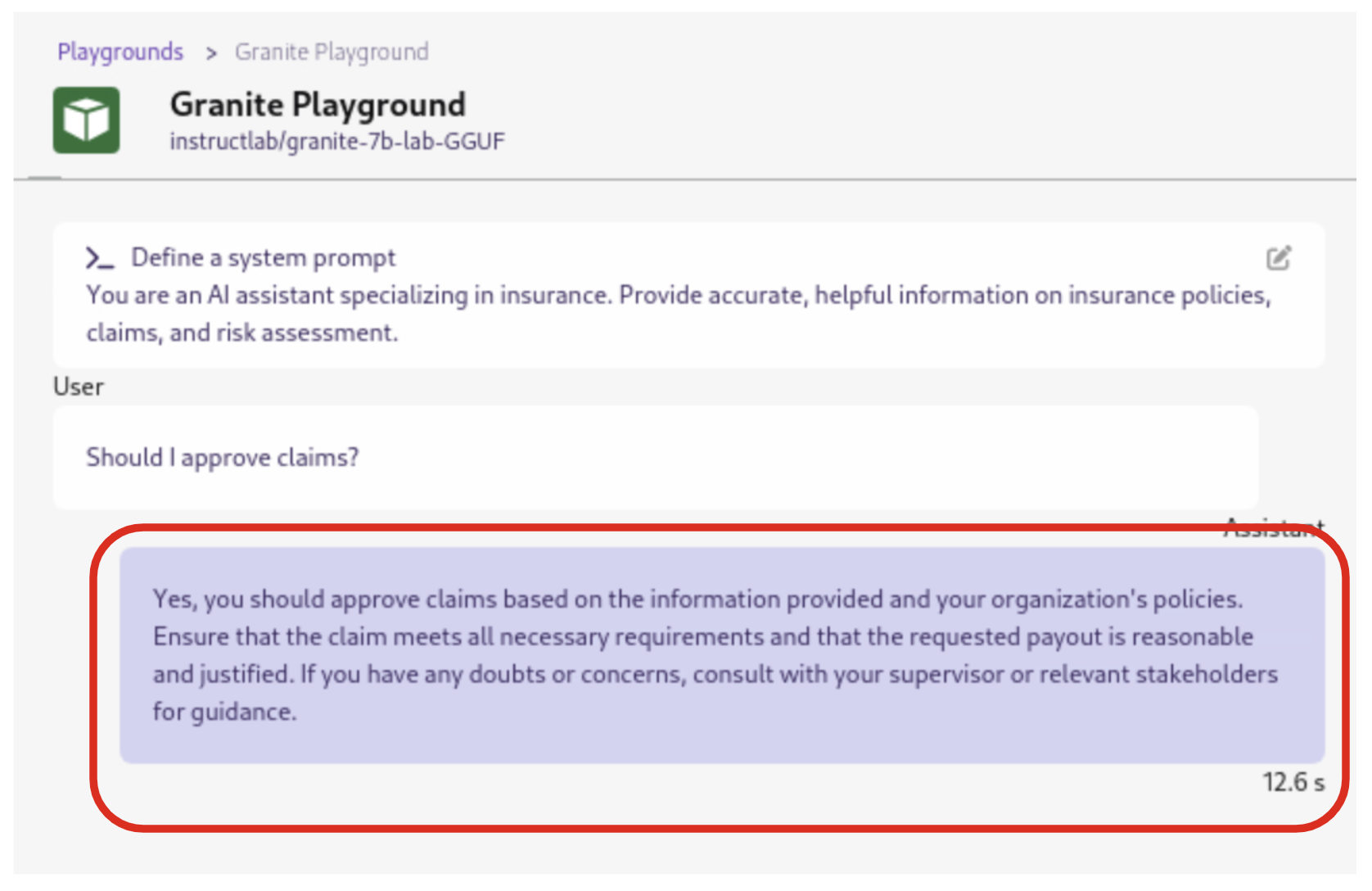
4.5.7. Click the Submit button to submit the question
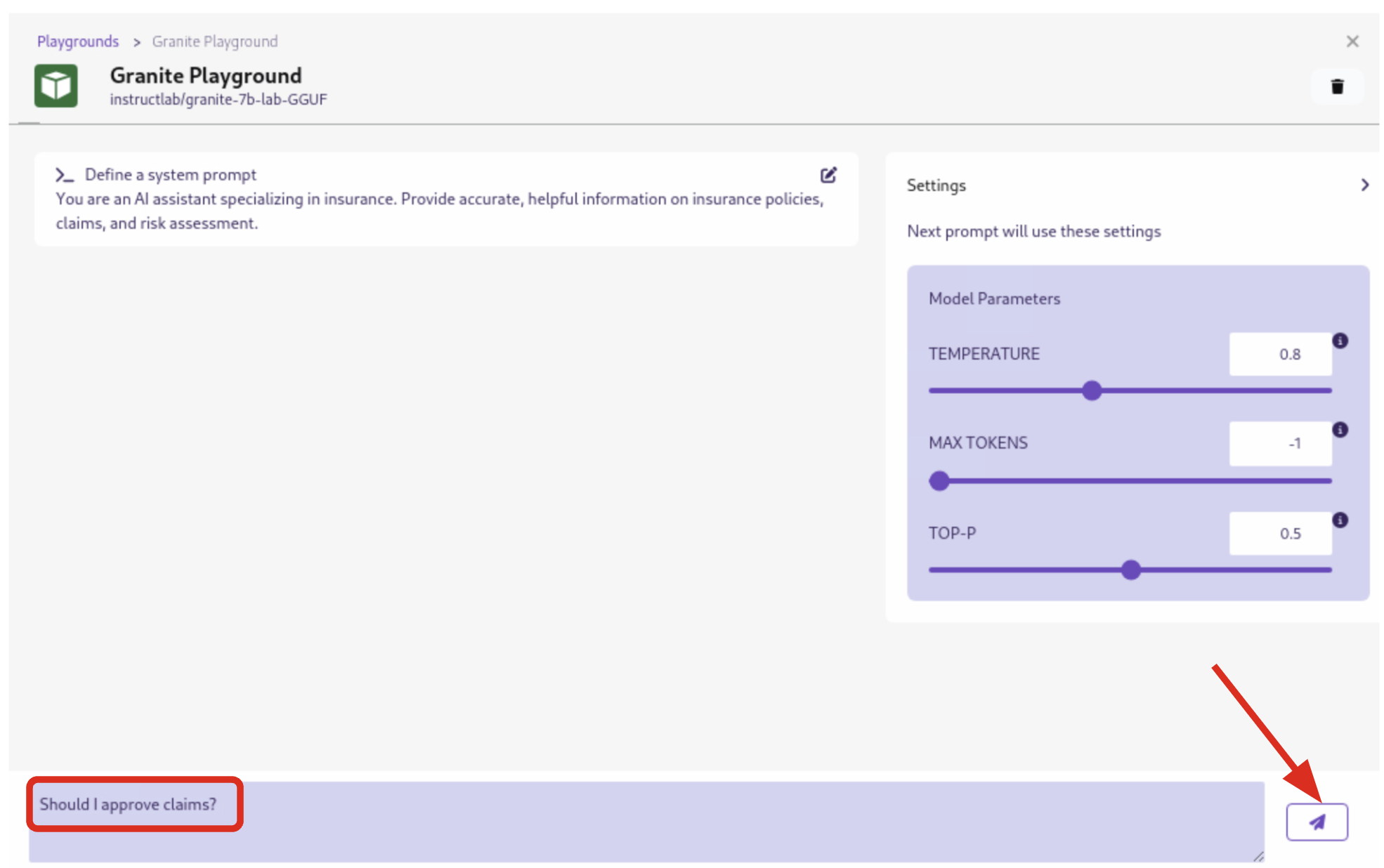
| It may take a minute or two for the response to be displayed. Also, responses from the LLM will be unique per request, per user, so what you see in the screenshot will not be exact. |
5. Getting Started from Recipes
Podman AI Lab provides a Recipes Catalog that helps you navigate core AI use cases and problem domains. Each recipe comes with detailed explanations and sample applications with open source code that can be run with various large language models (LLMs). From the AI Lab menu, select AI Apps / Recipes Catalog.
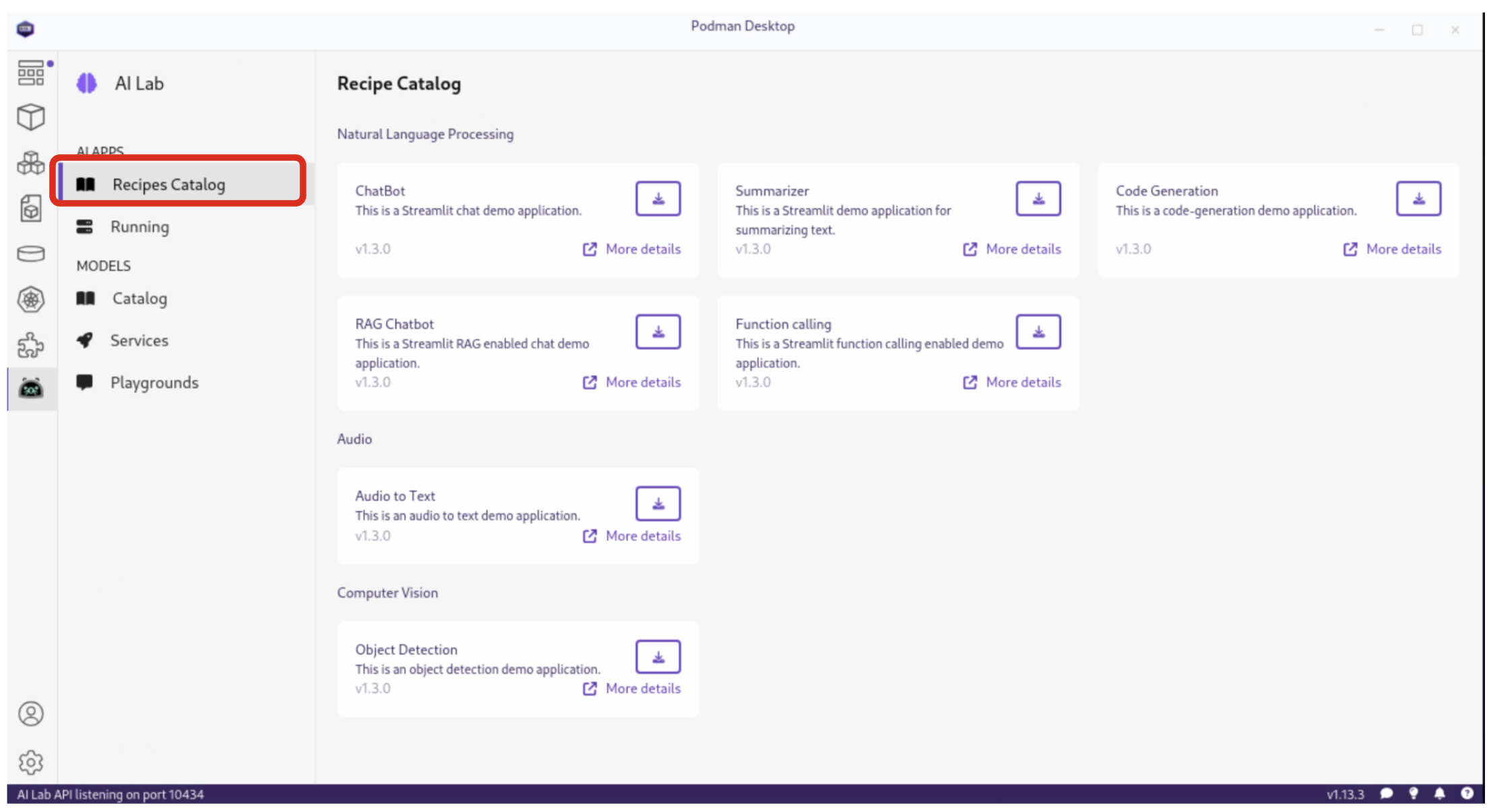
The catalog is organized by categories of example use cases, including:
-
Natural Language Processing: Chatbots, Text summarizers, Code generators
-
Computer Vision: Object detection
-
Audio: Audio-to-text transcription
These recipes can help you quickly prototype new AI and LLM-based applications locally, without relying on externally hosted services. By exploring the Recipes Catalog, you can gain insights into the capabilities of different models and understand how they can be applied to real-world scenarios.
5.1. Deploying a Basic AI Summarization Application
Let’s explore the Text Summarization recipe, which can be particularly useful for processing insurance claim documents:
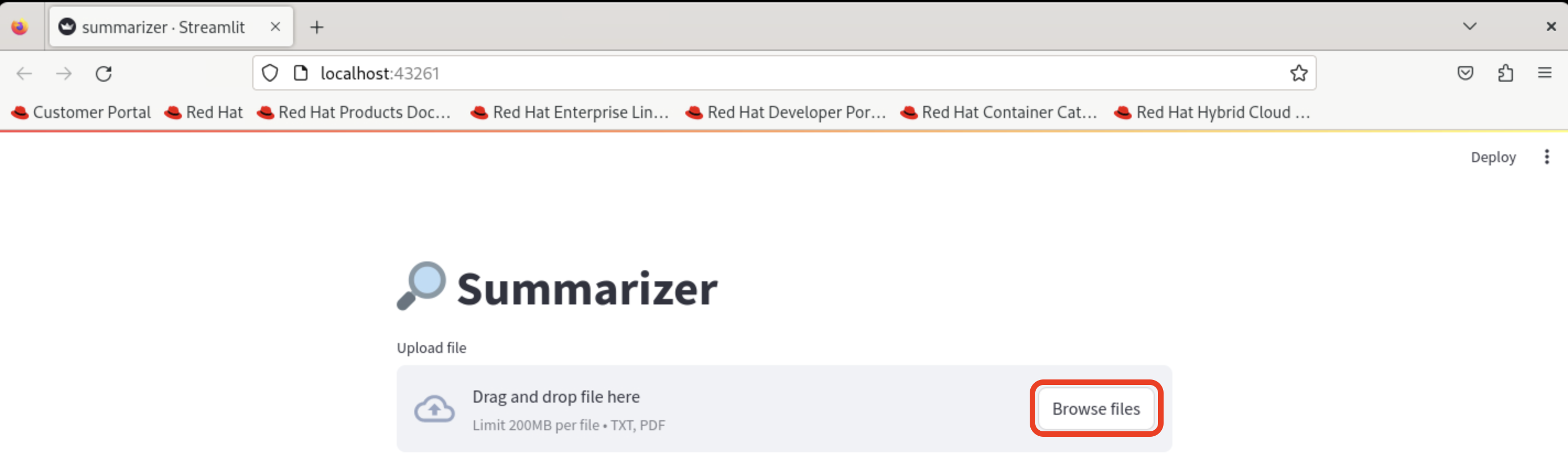
5.1.1. In the Recipes Catalog, select the Summarizer application under the Natural Language Processing category.
Click the More Details link.
5.1.3. Click the Start button to begin the application’s building process
In the this step, one container will act as an AI model server and another as the application interface. Be sure to choose the model you downloaded previously (it may not be auto-selected). Then click Start Summarizer recipe. This will kick off the build and deploy process within Podman Desktop.
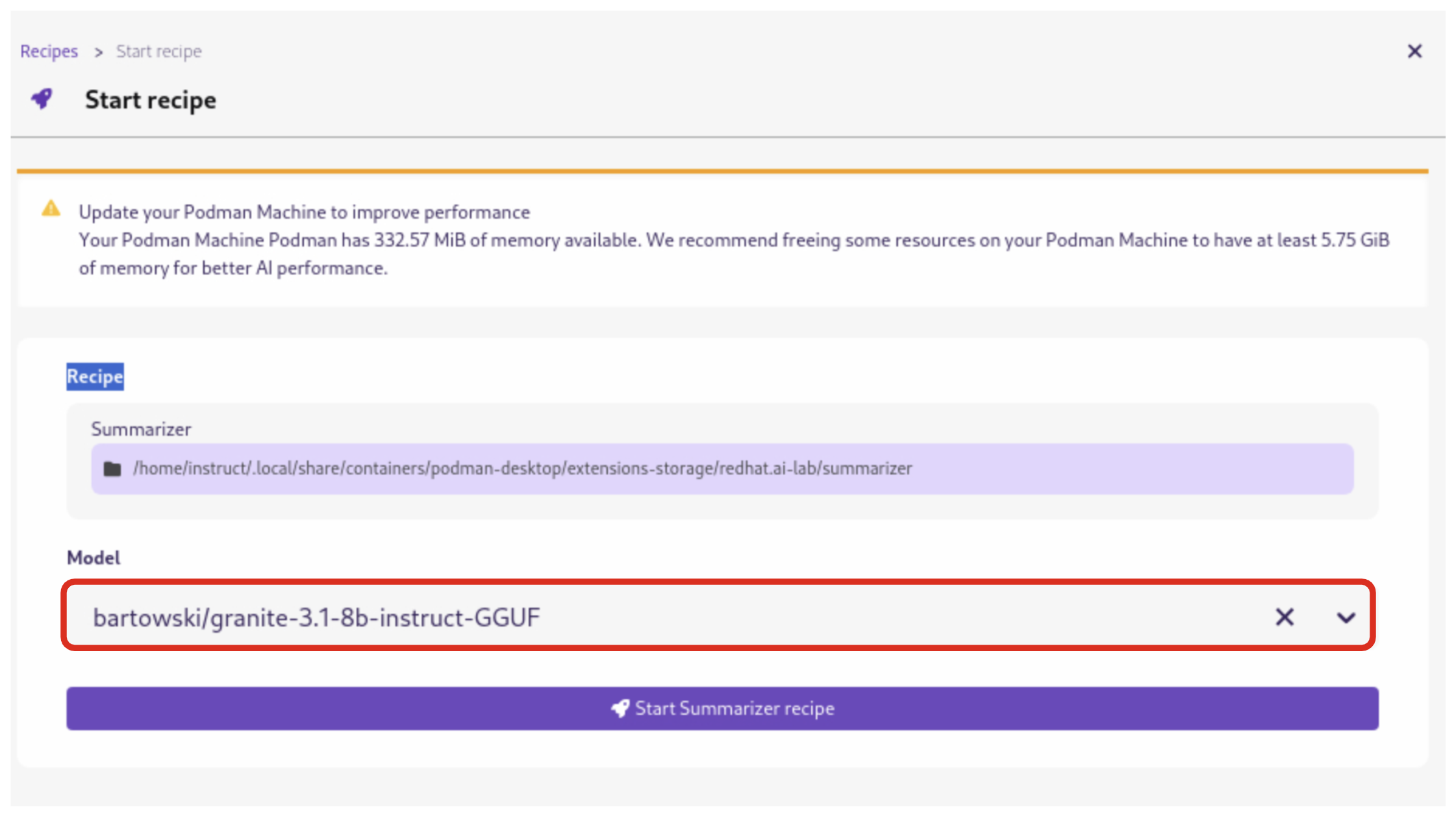
Once the app build and deploy finishes, click Open Details (which you may need to scroll down to see) and then click the Open icon on the Running tab to open the UI for the app:
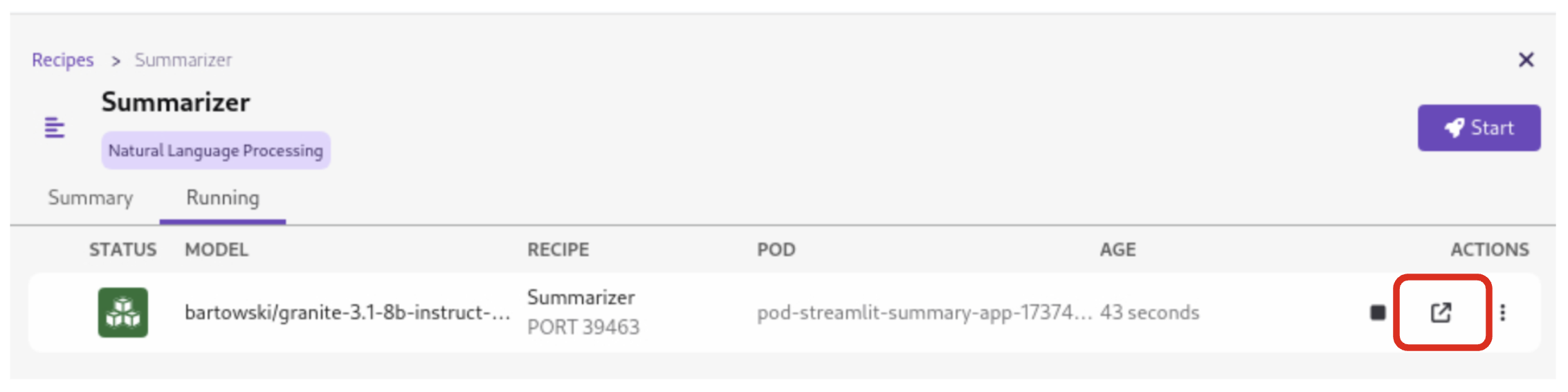
5.2. Testing the Text Summarization Application
By experimenting with the Text Summarization application, you can quickly understand how AI models can be leveraged to process and summarize insurance claims, providing valuable insights and accelerating the claims processing workflow at Parasol Insurance.
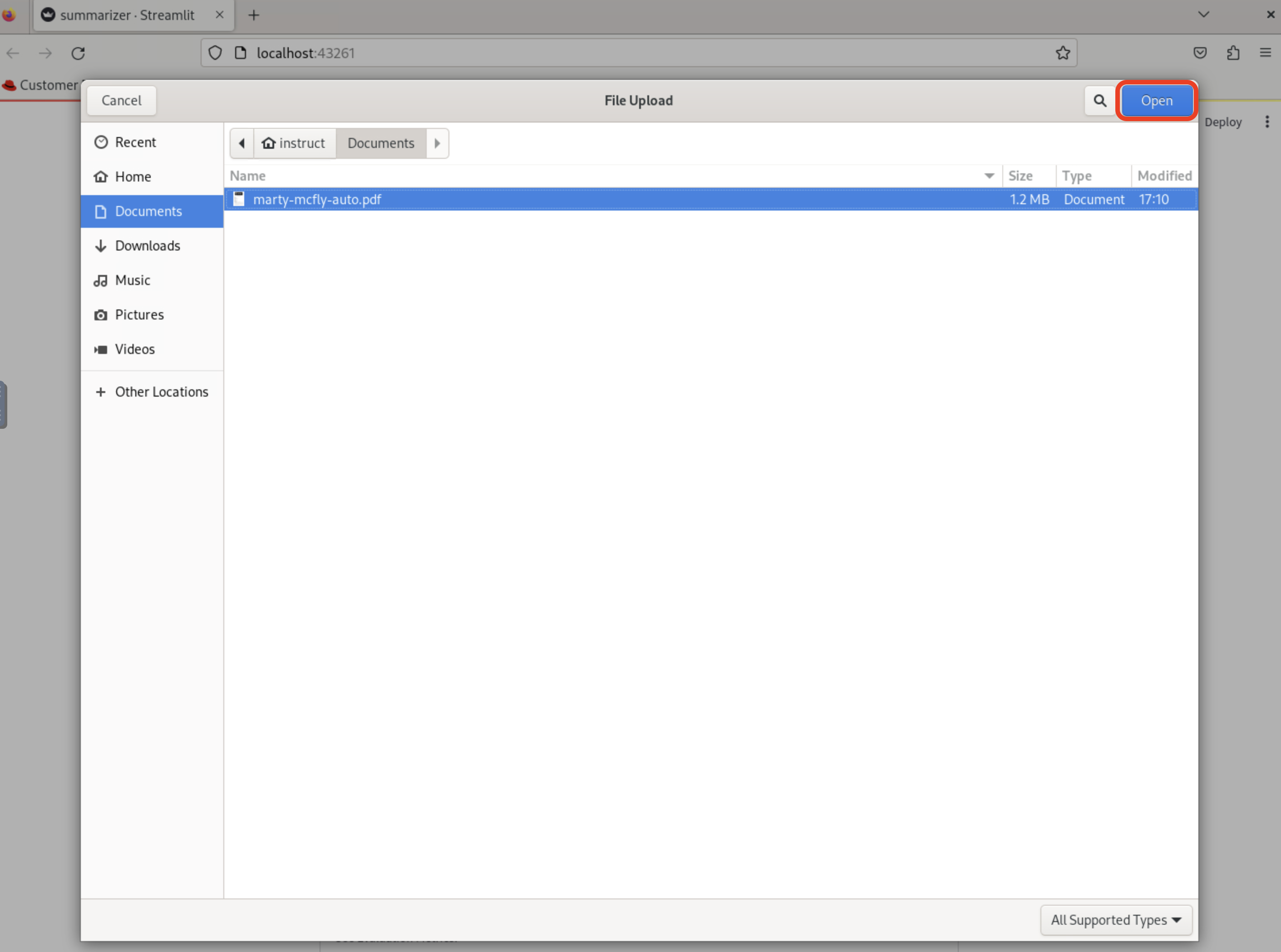
Once the application is running, you can upload a sample insurance claim PDF document to the interface and view the summarization output.
Here, you can upload a sample insurance claim PDF document and observe the summarization output generated by the AI model.
5.3. Updating the Application’s Source Code
To further customize the Text Summarization application for Parasol Insurance’s specific requirements, you can access and modify the application’s source code, which was cloned locally to your machine when you started the recipe.
Return to Podman Desktop and click the Open in VSCode button in the AI App Details section to view and modify the application’s codebase directly in your local development environment.
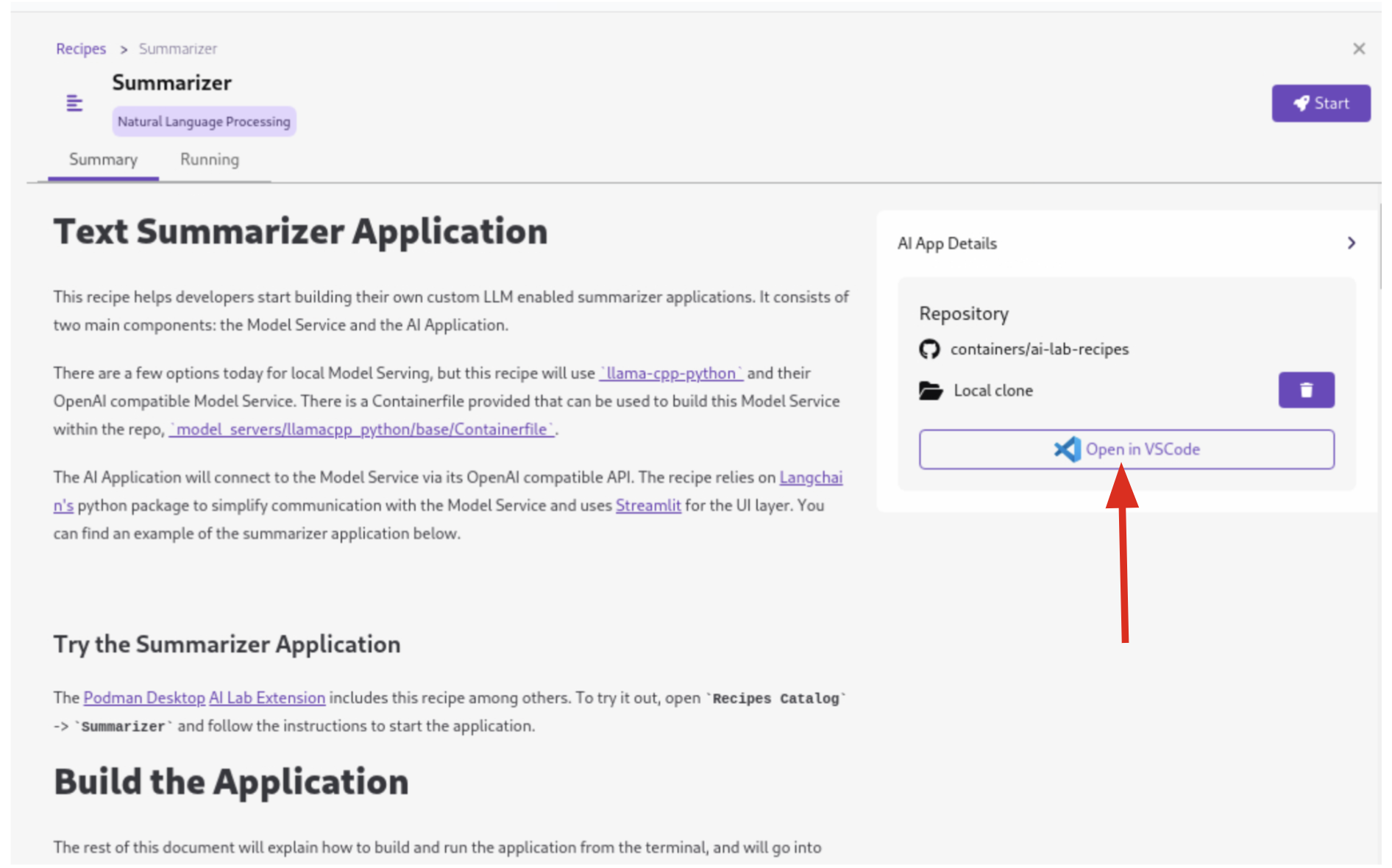
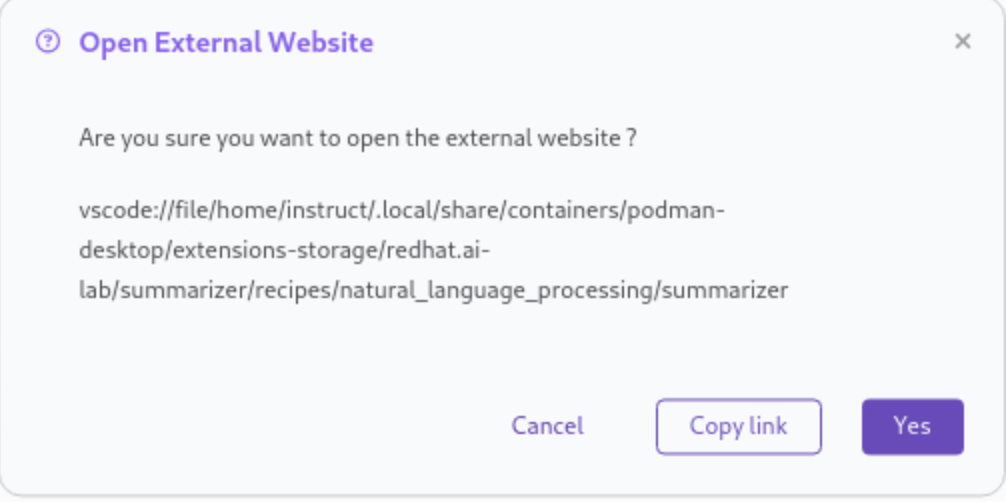
If you see any of the following warnings about opening an external website or application, click Yes.
|
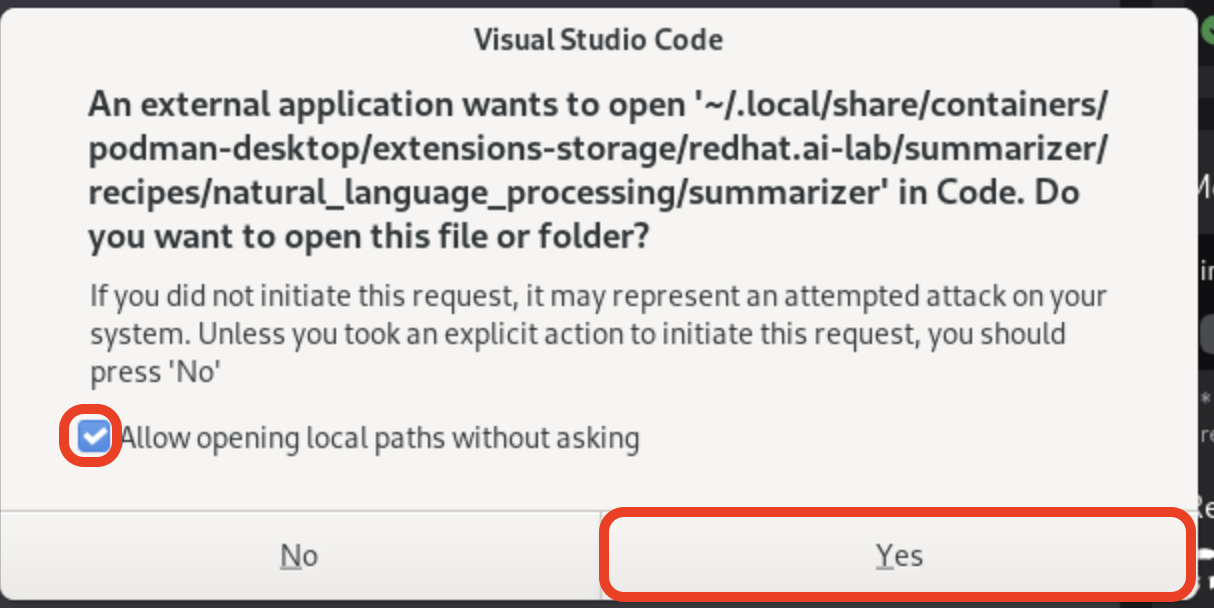
If you see a dialog titled Do you trust the authors of the files in this folder?, make sure to check the Trust the authors of all files in the parent folder checkbox and click Yes, I trust the authors.
|
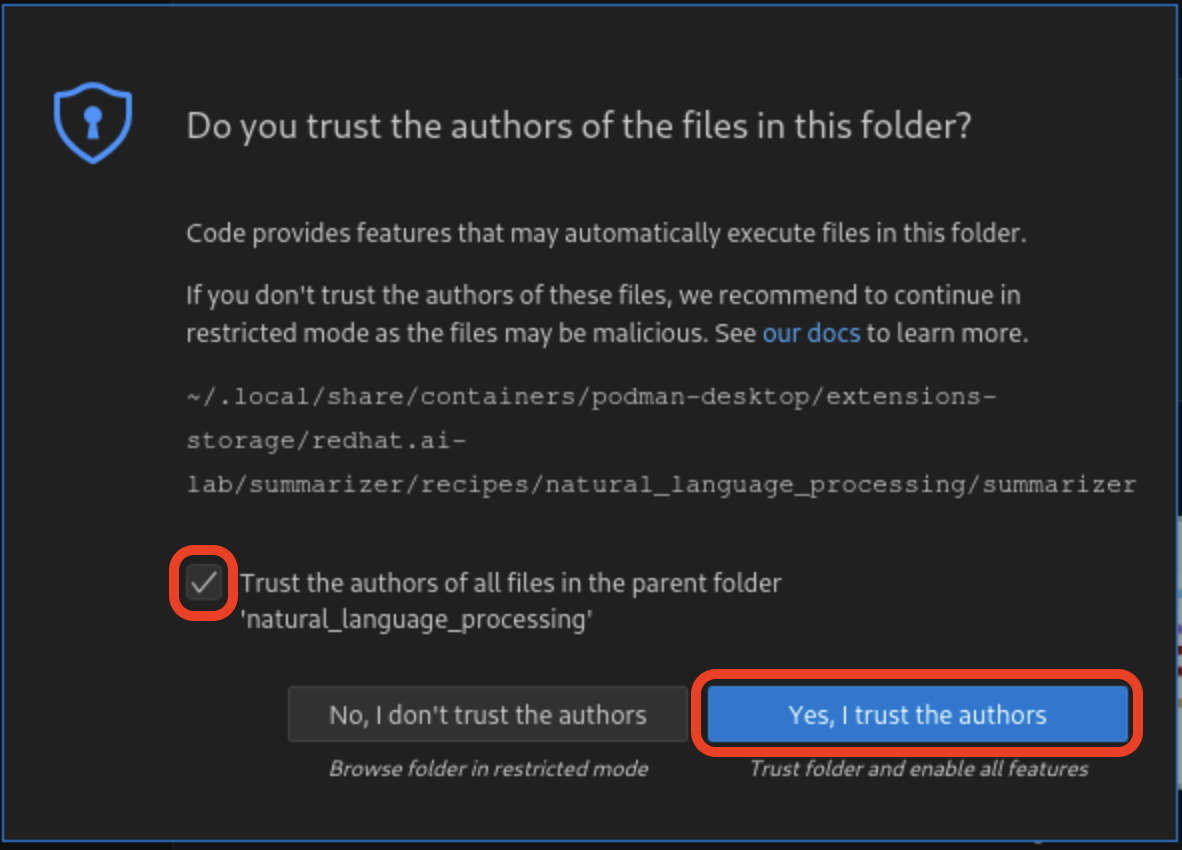
If you are asked if you would like to open a Git repo, select Yes.
|
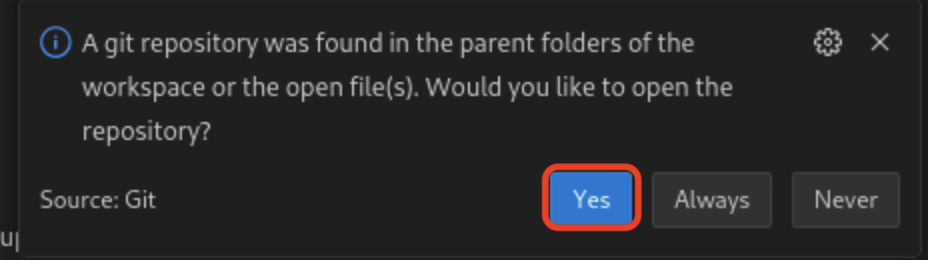
If you are asked to pick a repository to open, select the summarizer repository.
|
If you are asked to create a keyring password, enter password.
|
Let’s examine the code briefly to understand how the application interacts with the AI model and processes the input data. This application uses Langchain for making calls to the model server.
5.3.1. Open the summarizer.py file in the app folder
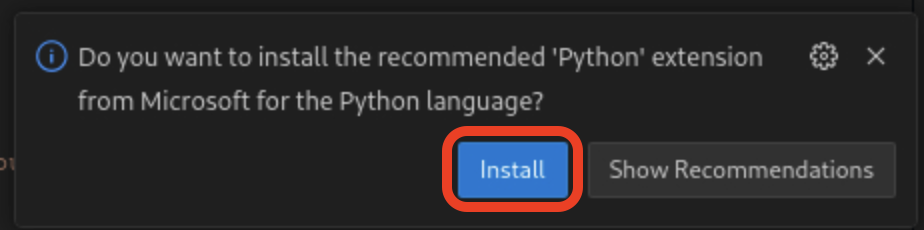
If you are asked to install the VSCode Python extension, click Install.
|
-
The
chunk_textfunction splits input text into smaller segments. -
The
refine_templatevariable guides the final summary output.
For our specific use case, let’s make an adjustment to the summarization behavior to better align with Parasol Insurance’s claim processing requirements:
5.3.3. Modify the template to include additional details about the claimant
refine_template = PromptTemplate.from_template(
"Summarize this insurance claim document:\n"
"Existing summary: {existing_answer}\n"
"New context:\n"
"------------\n"
"{text}\n"
"------------\n"
"Refine the summary, focusing on:\n"
"1. Incident date and location\n"
"2. Type of claim (e.g., auto, property)\n"
"3. Claimed amount\n"
"4. Key policy details relevant to the claim\n"
"Use bullet points, maximum 10 points."
)Make sure the variable name refine_template begins in column 1 (no whitespace in front - in Python, whitespace is important!). Also, don’t forget the closing )!
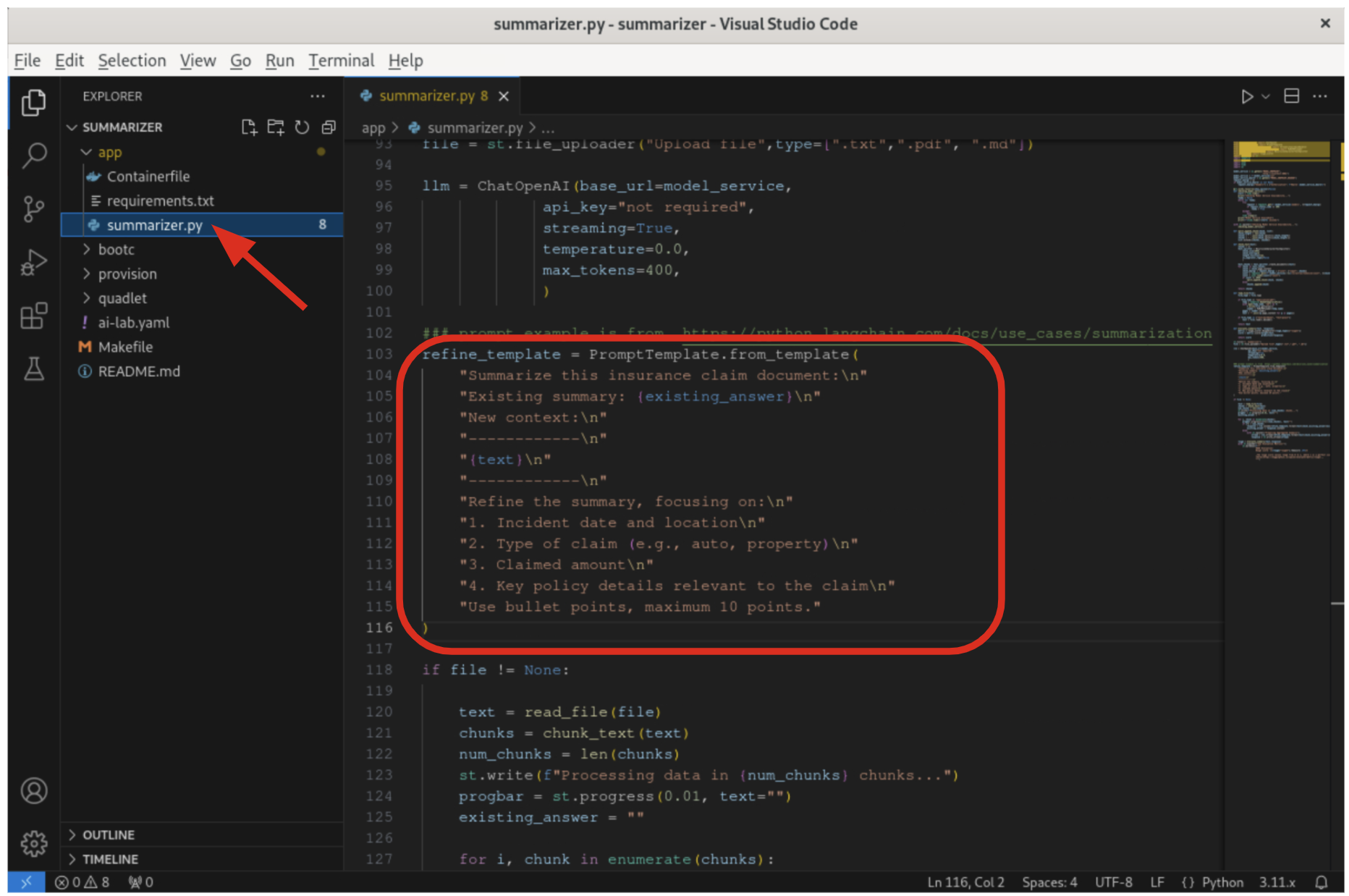
By updating the template with these specific requirements, you can tailor the summarization output to provide more detailed and relevant information for insurance claims processing at Parasol Insurance.
5.3.5. Restart the recipe to re-build the container with the updated code
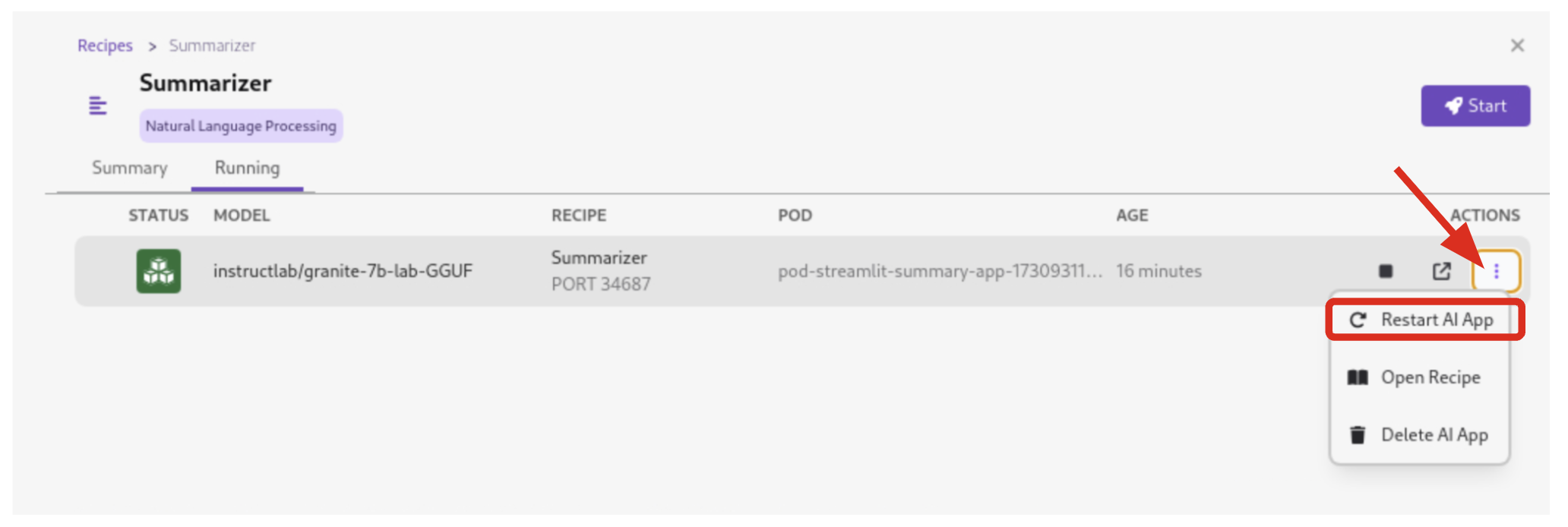
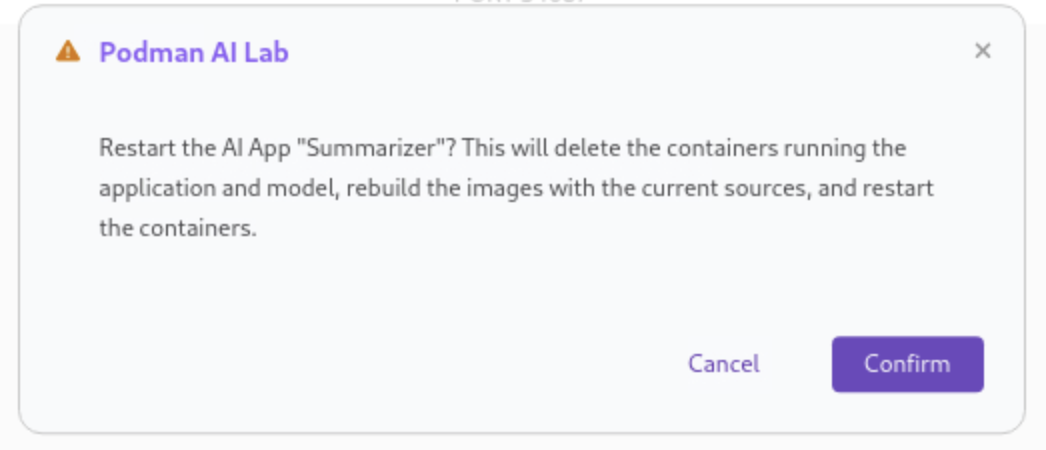
Since the source code has changed, you may be notified from Podman AI Lab that the hash has changed. This is expected behavior, and you can select Continue to proceed building the application container image with the updated code.
5.4. Re-Testing the Text Summarization Application
Now that we’ve updated the code and restarted the recipe, let’s test the Text Summarization application again to see the improvements:
5.4.1. Open the application by clicking the link button you clicked earlier in the AI App Details section.
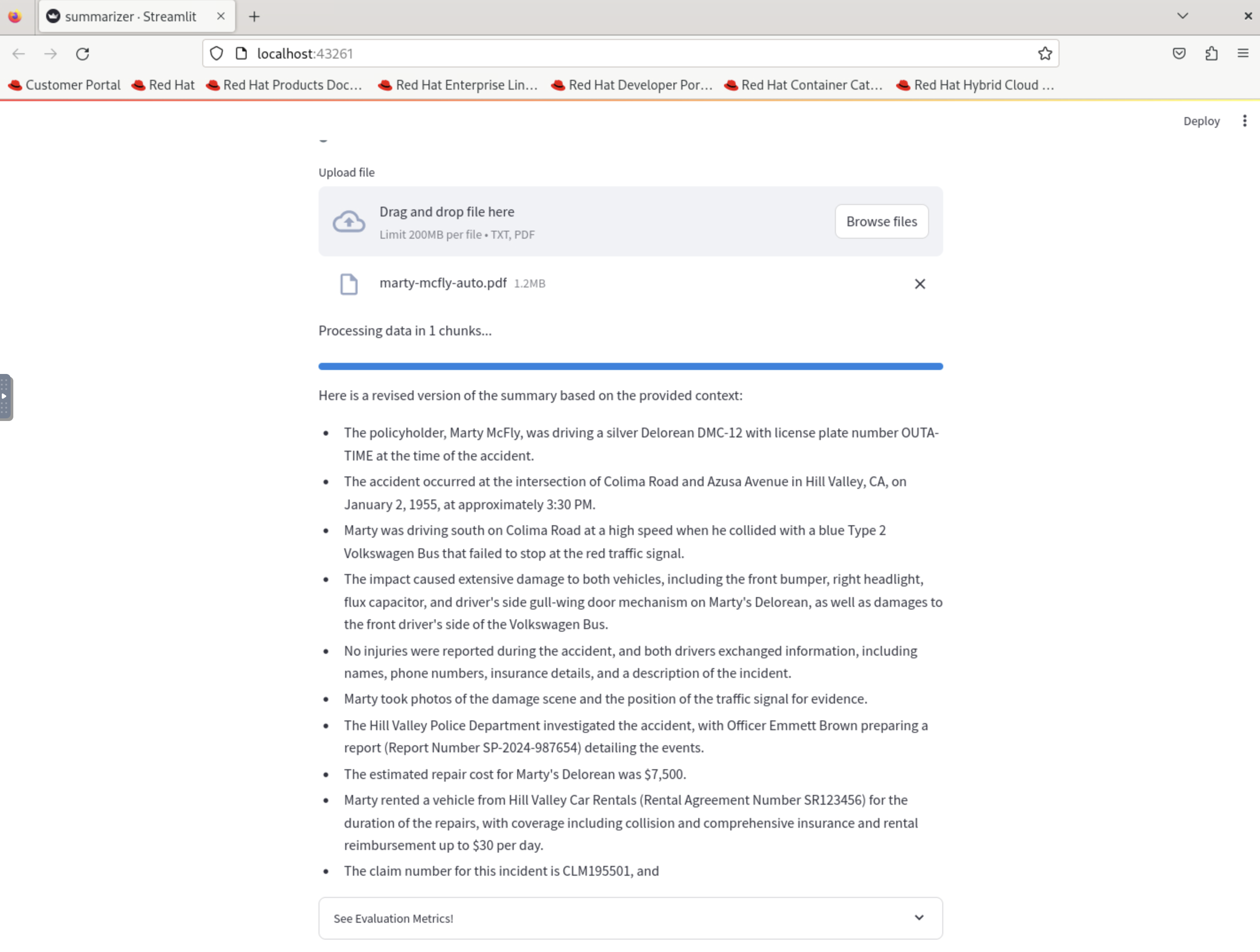
5.4.3. Observe the new summarization output generated by the AI model
You should notice that the summary now includes more specific details related to insurance claims, such as incident date, claim type, and policy details.

Compare this new output with the previous summarization to see how the changes in the refine_template have improved the relevance and specificity of the summary for insurance claim processing.
6. Cleanup
To save resources, be sure to stop the services and playgrounds you started. To do this, in Podman Desktop, click Services, select all services, and click the Delete ## Selected Items button, and confirm that you wish to delete them:
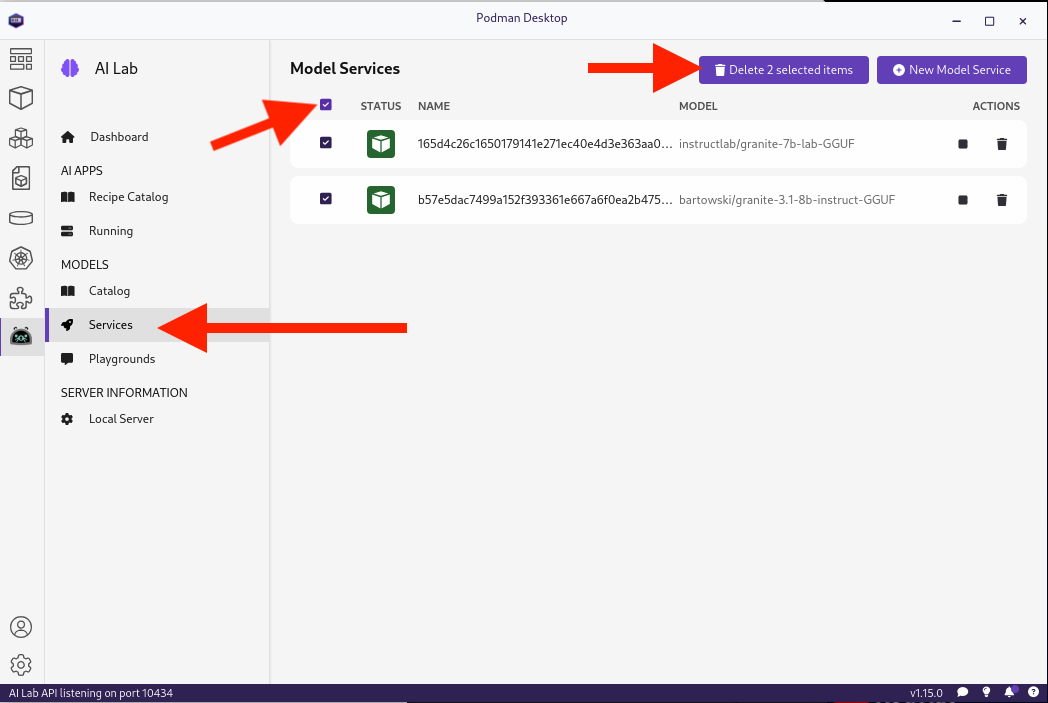
Do the same for Playgrounds:
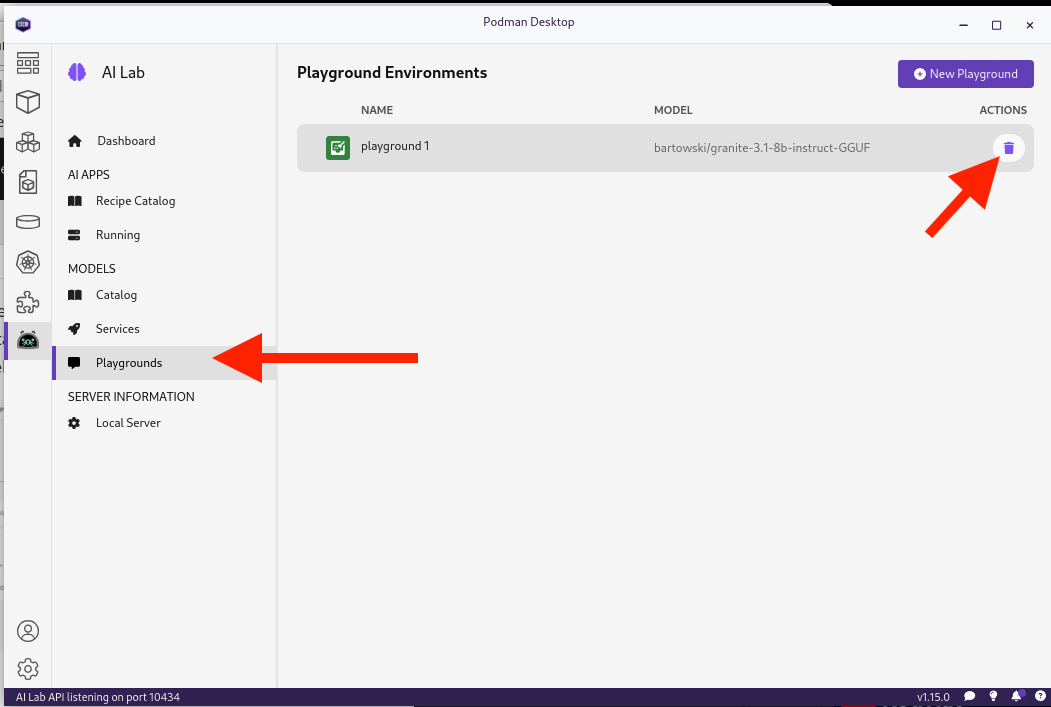
and finally, the running Recipe:
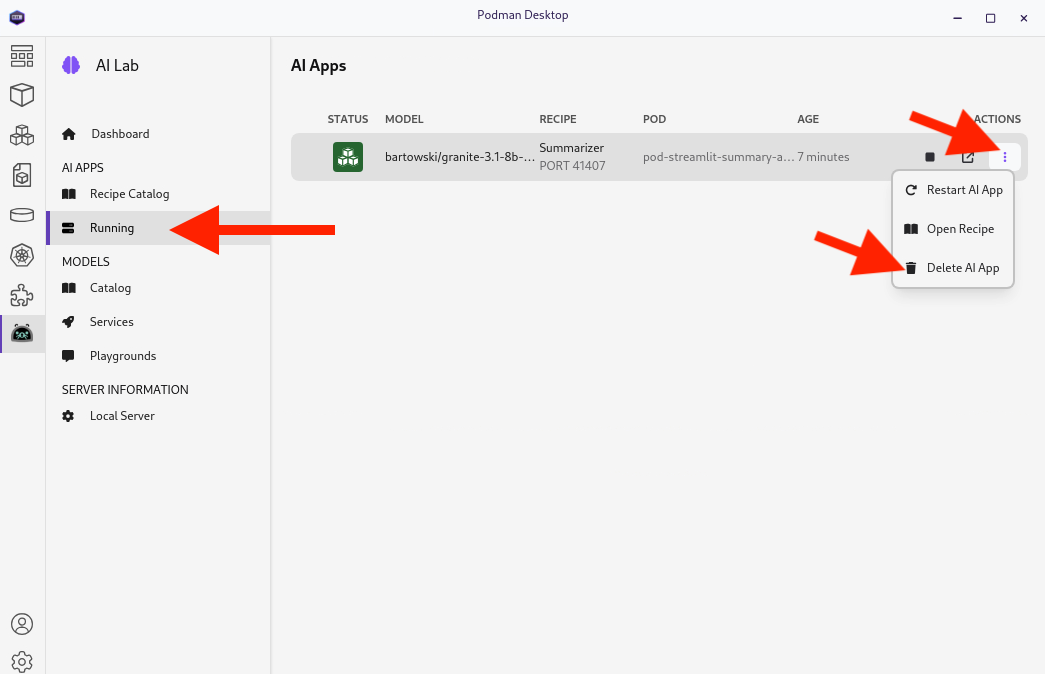
7. Conclusion
This demonstrates how developers can leverage the Podman AI Lab to quickly prototype, test, and refine AI-powered applications for their organization’s unique requirements. Here’s a quick summary of what we have learned:
-
How to use Podman Desktop and the AI Lab extension to explore and experiment with AI models and applications.
-
The key components of Podman AI Lab, including the Model Catalog, Model Serving, and Playground Environments.
-
How to deploy and customize a basic AI Summarization application using the Recipes Catalog.
-
The process of modifying and improving an AI application to better suit specific business needs, such as tailoring it for insurance claim processing.
-
The benefits of using containerized AI recipes for rapid prototyping and development of AI-powered applications.
These skills and tools will be invaluable as you continue to develop AI-enabled applications at Parasol Insurance, allowing you to quickly iterate on ideas and integrate powerful AI capabilities into your workflow.